What are the proximate causes of prosperity? How are they related to the fundamental causes of prosperity?
What will be an ideal response?
Proximate causes of prosperity are factors such as physical capital, human capital, and technology. They are referred to as proximate causes of prosperity because they link high levels of prosperity to high levels of the inputs of production, but without providing an explanation as to why the levels of those inputs are high.
Proximate causes of prosperity arise out of fundamental causes of prosperity. Fundamental causes of prosperity are factors that are at the root of the differences in the proximate causes of prosperity.
You might also like to view...
The marginal product of capital (MPK) measures ________
A) by how much output increases for each additional unit of capital B) by how much capital increases for each additional unit of output C) by how much capital increases for each additional unit of labor D) by how much total factor productivity increases for each additional unit of capital E) none of the above
Which of the following statements is correct?
a. Public ownership is preferred to regulation in order to minimize the deadweight losses associated with natural monopolies. b. Antitrust laws are always the best way to limit monopoly power. c. It is possible that the best approach to monopolies is for the government to do nothing. d. Marginal-cost pricing requires a natural monopoly to earn zero economic profits.
Which price structure would tend to most effectively promote water conservation?
a. Uniform block structure b. Constant price structure c. Increasing block structure d. Decreasing block structure e. Marginal price structure
The profit-maximizing/loss-minimizing level of output
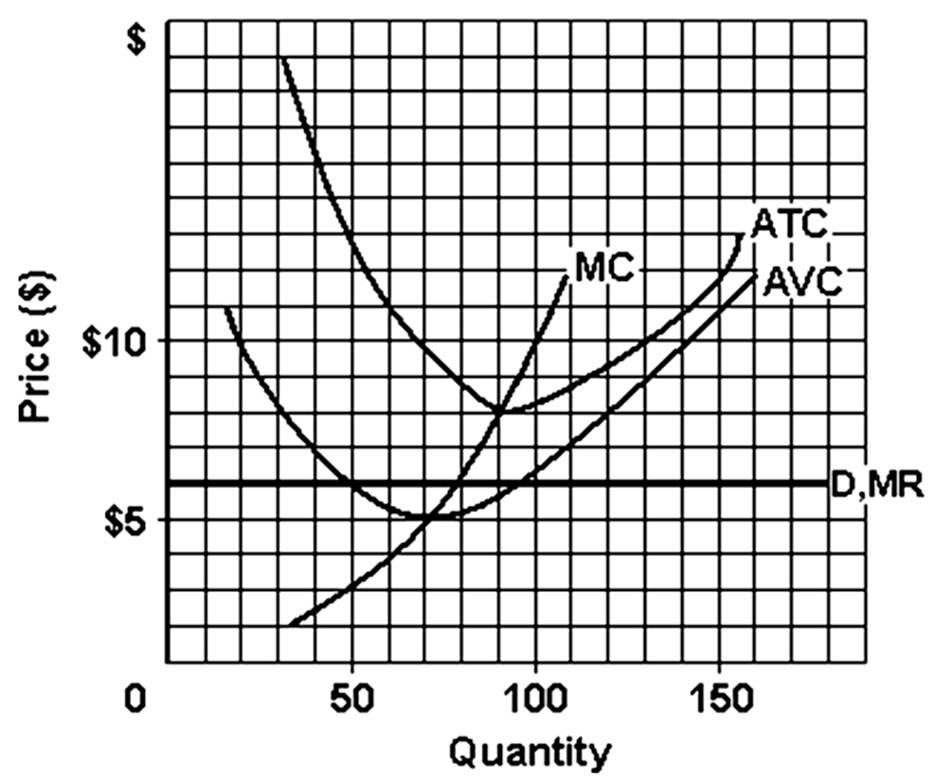
A. is 70 units.
B. is 80 units.
C. is 90 units.
D. cannot be determined with this graph.