Use the figure below to answer the next question. 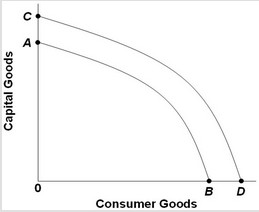 An increase in an economy's labor productivity would
An increase in an economy's labor productivity would
A. shift the production possibilities frontier from CD to AB.
B. move the economy away from point B and toward point A.
C. shift the production possibilities frontier from AB to CD.
D. move the economy away from point A and toward point B.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The figure below shows the market for shoes in a small importing country. Dd and Sd are the domestic demand and supply curves of shoes, respectively.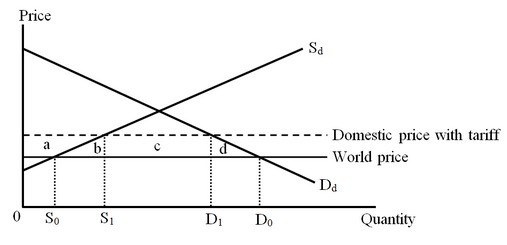 The consumption effect of the tariff on shoes is measured by the area
The consumption effect of the tariff on shoes is measured by the area
A. b. B. c. C. (a + b + c + d). D. d.
In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the
equilibrium quantity (Q) of X. Refer to the given information. If X is an inferior good, a decrease in income will: A. decrease D, decrease P, and decrease Q. B. decrease D, decrease P, and increase Q. C. increase S, decrease P, and increase Q. D. increase D, increase P, and increase Q.
Refer to the graph showing the demand for books. If the price is changed from $12.00 to $4.00, the quantity demanded increases by: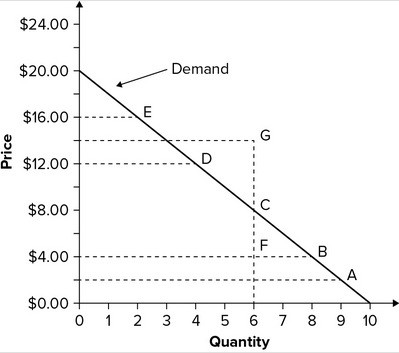
A. 6 books. B. 8 books. C. 2 books. D. 4 books.
The basic proposition in international trade is that
A) trade is determined by absolute advantage. B) in the long run, imports are paid for by exports. C) everyone is made better off by free trade. D) fair trade is more important than free trade.