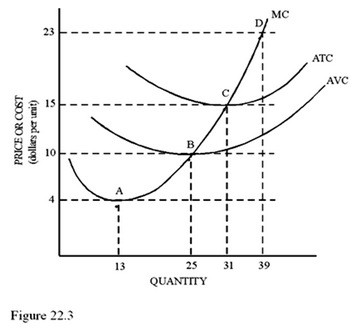
 Refer to Figure 22.3 for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is $23,
Refer to Figure 22.3 for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is $23,
A. Economic profits are zero.
B. The firm will have above-normal profits.
C. The firm should produce 31 units.
D. The firm should produce 25 units.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The U.S. government can continue to run a deficit as long as the cost of servicing the resulting debt remains manageable
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Monopolistic competition and perfect competition are different in that monopolistically competitive firms: a. cannot earn profits in the short run
b. face firm demand curves that are less elastic than perfectly competitive firms. c. face substantial barriers to entry. d. earn economic profits in the long run.
Which of the following best describes the situation likely to unfold after a new manufacturing firm enters an oligopolistic market?
a. The new firm is initially hampered by economies of scale. b. The new firm initially has low costs of production that increase over time. c. The new firm has high sales during its early years followed by a sales decline. d. The new firm is initially very profitable.
BMW recently decided to build a manufacturing plant in Shenyang, China. At this plant, BMW is able to take advantage of paying lower wages to its Chinese workers than it pays its German workers, but it also sacrifices the high levels of technical training possessed by its German workers. In deciding to open the Shenyang plant, BMW
A) faced no trade-offs because employing lower-wage workers increased efficiency. B) eroded some of its competitiveness in the luxury car market because of its decreased cost of production. C) faced a trade-off between higher cost and lower precision. D) adopted a negative technological change because it replaced high-skilled workers with low-skilled workers.