If the company plans to produce 5000 units of output, is using the competitor's technology a good idea?
a. Yes
b. No
c. It does not matter, at 5000 units you are indifferent between the two technologies
d. None of the above
b
You might also like to view...
Ceteris Paribus, if current output has fallen below potential ________
A) a positive inflation gap will ensue B) it is likely that the equilibrium real rate has fallen below the policy rate C) a negative unemployment gap will ensue D) it is likely that the equilibrium real rate has risen above the policy rate E) none of the above
The user cost of an exhaustible resource is
A) the same as its price. B) the same as its production cost. C) the opportunity cost of using the resource today rather than saving it for the future. D) the amount of the resource that is extracted today. E) not related to the amount of the resource that exists.
Airlines are __________ than they were before deregulation
a. more dangerous b. more concentrated c. higher priced d. flying fewer miles e. much more profitable
Figure 6-1
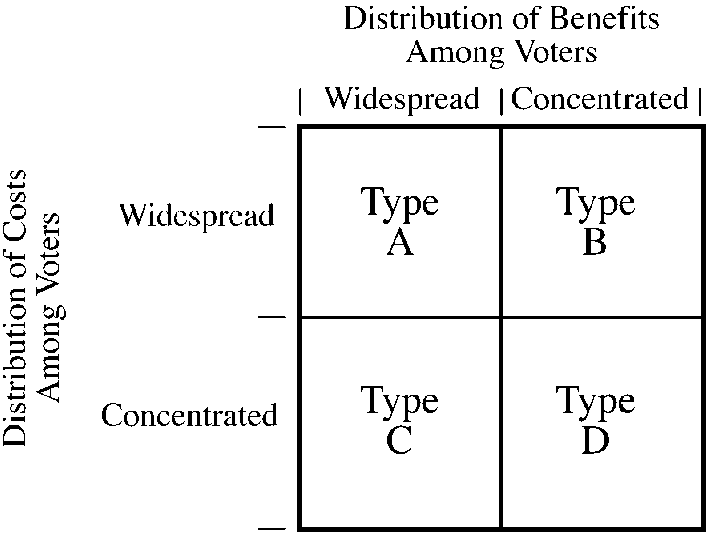
illustrates the four possibilities of the distribution of costs and benefits among voters for a government project. Programs that give subsidies to a small group of producers at general taxpayer expense would be considered
a.
type A projects, and the government would be likely to undertake these projects if they were efficient and to reject them if they were inefficient.
b.
type B projects, and the government would be likely to undertake many of these projects even when they were counterproductive (inefficient).
c.
type C projects, and the government would be likely to fail to undertake many of these projects even when they were productive (efficient).
d.
type D projects, and the government would be likely to undertake these projects if they were efficient and to reject them if they were inefficient.