Some countries win in international trade, while other countries lose
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
False
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is true?
A) The price charged by a monopolistically competitive firm is equal to the price charged by a perfectly competitive firm in the long run. B) The price charged by each firm in a monopolistically competitive market is equal in the long run. C) The profit earned by a firm in a monopolistically competitive market is equal to the profit earned by a firm in a perfectly competitive market in the long run. D) The profit earned by a firm in a monopolistically competitive market is equal to the profit earned by a monopolist in the long run.
What is the relationship between marginal cost and marginal product?
a. The two are not related. b. When marginal product increases, marginal cost increases. c. When marginal product increases, marginal cost falls. d. When marginal product is negative, marginal costs are negative. e. When diminishing marginal returns set in, marginal costs fall.
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) Other things being equal, society's overall well-being is reduced when a perfectly competitive industry is monopolized. B) When both a perfectly competitive industry and a monopolist face the same production costs and the same market demand curve,the monopolist offers a lower level of output for sale. C) The profit-maximizing monopolist will always produce only along the inelastic portion of the demand curve, whereas equilibrium in a perfectly competitive industry always occurs along the elastic portion of the demand curve. D) When both a perfectly competitive industry and a monopolist face the same production costs and the same market demand curve, the monopolist charges a higher price for its product than what would be charged in a perfectly competitive situation.
Refer to the diagram. If eurozone nations decide to import more agricultural products from the United States, we would expect:
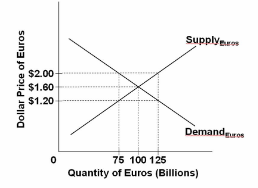
A. the demand for euros to increase and the euro to appreciate.
B. the demand for euros to increase and the dollar to appreciate.
C. the supply of euros to increase and the euro to depreciate.
D. the supply of euros to decrease and the dollar to depreciate.