Use the graph below to explain the relationship between investment and the multiplier. Increases in investment are in $20 billion shifts. The slope of the aggregate expenditure curve is 0.75.
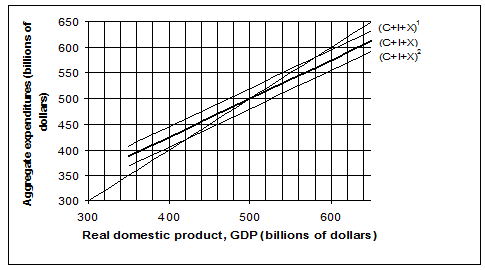
The graph shows that a small shift in investment, possibly due to a change in expected returns or the interest rate, causes a large shift in GDP. Looking at the graph, a decrease in investment by $20 billion dollars from (C+I) to (C+I)2 causes a decrease in GDP of $80 billion. Conversely, an increase in investment from (C+I) to (C+I)1 causes an increase in GDP of $80 billion (from $580 billion to $500 billion). Given that the slope of the aggregate expenditures curve is 0.75, we know that the marginal propensity to consume is also 0.75. Using the equation to calculate the multiplier (1/(1 ? MPC)) we find the multiplier to be 4. We can also find this using our results from the shifts in investment, dividing the change in GDP by the change in investment (80/20 = 4). We also know that the marginal propensity to save is .25, meaning that an $80 billion increase in income causes a $20 billion increase in savings. This increase in savings helps bring the economy back in equilibrium, where savings equals investment and C+I=GDP.
You might also like to view...
The accounting system requires that the current account and the financial account sum to ________
A) 0 B) 1 C) 100 D) 10
Why does the return to capital change after trade occurs?
a. There is more labor used per unit of capital in the manufacturing sector. b. There is more capital used per unit of labor in the manufacturing sector. c. There is more labor used per unit of land in the agricultural sector. d. There is more land used per unit of labor in the agricultural sector.
Which of the following efforts did the Clinton administration embrace?
A. Reduction in immigration of highly skilled workers. B. Increase in taxes on capital gains. C. Expansion of the money supply. D. "New Direction" tax increases and spending cuts
Assume that Anna buys peanut butter and bread. If the price of peanut butter falls, then
A. One end of her budget constraint will move away from the origin. B. Her entire budget constraint will shift away from the origin. C. Her entire budget constraint will shift toward the origin. D. Her indifference curves will shift away from the origin.