Inferring stellar lifetimes: Scientists must often draw on a variety of concepts to develop new understanding. Take, for example, the inferred lifetimes of stars
What two properties must be precisely measured in order to estimate the lifetime? Outline the set of observations that must be made in order to determine those properties. Then discuss the fundamental physics that must be understood to relate these to the rate at which hydrogen is converted to helium in the stellar core, and to determine the amount of hydrogen available in the core.
Should include description of the measurements of apparent brightness and distance to determine luminosity, and observations of eclipsing binaries to determine stellar masses. Then the answer should reference the known energy release from each set of four hydrogen nuclei converted to helium, and the importance of understanding the behavior of gases to predict how much of the star's mass is in the high pressure / high temperature core.
You might also like to view...
An iron block in a furnace is heated and consequently expands, which means that its density is
A) less. B) the same. C) more.
A CD with a diameter of 12.0 cm starts from rest and with a constant angular acceleration of 1.00 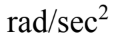 acquires an angular velocity of 5.00 rad/sec. The CD continues rotating at 5.00 rad/sec for 15.0 seconds and then slows to a stop in 12.0 second with a constant angular deceleration. What is the angular distance traveled by a point 4.00 cm from the center, at the time 10.0 seconds from the start?
acquires an angular velocity of 5.00 rad/sec. The CD continues rotating at 5.00 rad/sec for 15.0 seconds and then slows to a stop in 12.0 second with a constant angular deceleration. What is the angular distance traveled by a point 4.00 cm from the center, at the time 10.0 seconds from the start?
A. 20.8 radians B. 26.3 radians C. 37.5 radians D. 41.6 radians E. 47.3 radians
Aberration: Spherical lenses suffer from
A. both spherical and chromatic aberration. B. spherical aberration, but not chromatic aberration. C. chromatic aberration, but not spherical aberration. D. neither spherical nor chromatic aberration.
Light passes from a material with index of refraction 1.1 into one with index of refraction 1.5 after being incident at a non-normal angle (?inc ? 0). Compared to the incident ray, the refracted ray will
1.be unaffected. 2.bend towards the normal. 3.follow the normal. 4.bend away from the normal.