From 1900 to 1960, Latin America's real GDP grew
A) slower than Europe, Asia, and the U.S.
B) as fast or faster than Europe, Asia, and the U.S.
C) faster than Europe and the U.S. but slower than Asia.
D) faster than Asia, but slower than Europe and the U.S.
B
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a tax cut that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ and eventually to a long-run equilibrium at point ________, if left to self-correcting tendencies. 
A. D; C B. B; C C. B; A D. D; B
The gross domestic product of a country is $500,000. If its income per worker of the population is $100, the size of its employed labor force is ________
A) 5,000 B) 200 C) 8,000 D) 2,500
According to the graph shown, if the economy were open to free trade, the domestic quantity supplied would:
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good, as well as a tariff and the world price for that good.
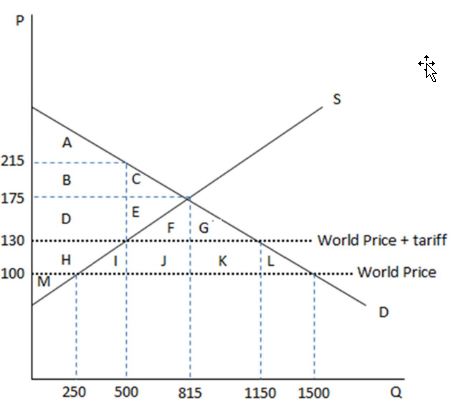
A. drop from 815 to 500.
B. drop from 815 to 250.
C. increase from 250 to 500.
D. increase from 815 to 1500.
In some countries it is time consuming and costly to establish ownership of property. Reforms to reduce these costs would likely
a. have no affect on either real GDP nor productivity b. raise real GDP and productivity. c. raise real GDP but not productivity. d. raise productivity but not real GDP.