In the Stackelberg model,
A. one firm plays a leadership role and its rivals merely react to the leader's quantity.
B. each firm takes the quantities produced by its rivals as given.
C. prices are higher and quantities are slightly less than we would see if the firms colluded to achieve the monopoly outcome.
D. each firm takes the prices charged by its rivals as given.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a tax cut that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ and eventually to a long-run equilibrium at point ________, if left to self-correcting tendencies. 
A. D; C B. B; C C. B; A D. D; B
Investment is the expenditure done by
A) savers. B) firms. C) the rest of the world. D) governments. E) Both answers A and B are correct.
Suppose GE produces 1 million light bulbs per month While labor is variable both in the short run and the long run, capital is fixed in the short run. Labor is sold at a rate w and capital is rented at a rate r. a. On a graph with labor on the horizontal axis, illustrate the current isocost and isoquant for GE. Carefully label the slope of the isocost. b. For the rest of the problem, suppose a new tax on capital is implemented but GE intends to continue to produce 1 million light bulbs per year. What will GE do differently in the short run and the long run? Explain using your graph from part (a). c. Using your answer to part (b), explain what happens to the short run cost curve in the short run. What happens to this short run curve in the long run? Do costs rise more or less in the
long run than they do in the short run? d. Do total costs rise more or less in the long run than total expenditures do in the short run? Explain. What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the information provided in Figure 17.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 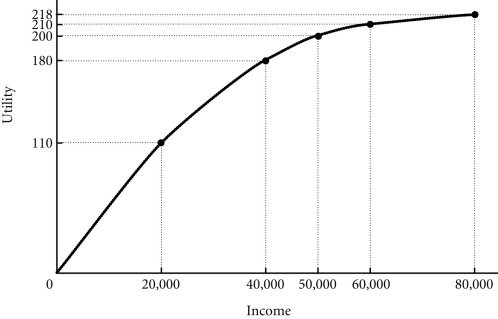 Figure 17.1 Refer to Figure 17.1. Dmitri has two job offers when he graduates from college. Dmitri views the offers as identical, except for the salary terms. The first offer is at a fixed annual salary of $40,000. The second offer is at a fixed salary of $20,000 plus a possible bonus of $40,000. Dmitri believes that he has a 50-50 chance of earning the bonus. Dmitri's expected utility from the first job offer is ________ and it is ________ from the second job offer.
Figure 17.1 Refer to Figure 17.1. Dmitri has two job offers when he graduates from college. Dmitri views the offers as identical, except for the salary terms. The first offer is at a fixed annual salary of $40,000. The second offer is at a fixed salary of $20,000 plus a possible bonus of $40,000. Dmitri believes that he has a 50-50 chance of earning the bonus. Dmitri's expected utility from the first job offer is ________ and it is ________ from the second job offer.
A. 180; 160 B. 180; 210 C. 180; 110 D. 90; 160