If a firm produces a good and then adds it to its inventory rather than selling it, for the purposes of GDP accounting the firm is considered to have "purchased" the good so it will count as part of that period's investment expenditures
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
True
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is TRUE about producers' willingness to offer warranties on products?
A) Producers are equally likely to offer warranties on high-quality and low-quality goods. B) Producers are more likely to offer warranties on low-quality goods, because without the signal that the warranty provides, the low-quality good wouldn't sell. C) Producers are more likely to offer warranties on high-quality goods, because the expected cost of repairs is lower for those goods. D) Producers have an incentive to deal with third-party companies to provide the warranties, so that an "impartial" view of the product is given to the consumer. E) Producers will not offer warranties in any market that suffers from asymmetric information.
The school of thought that emphasizes the natural tendency for an economy to move toward equilibrium full employment is known as the:
A. Keynesian school. B. supply-side school. C. rational expectations school. D. classical school.
Figure 33-8
?

A. A B. B C. C D. E
In Table 17.1, Brazil has 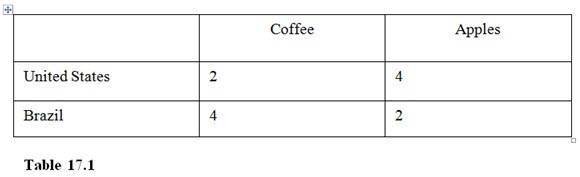
A. an absolute and comparative advantage in coffee. B. an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods. C. an absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in coffee. D. an absolute and comparative advantage in apples.