Sometimes the outermost layers of a pulsating variable star are too opaque to allow much energy to escape to space. What happens to the star as a consequence of this?
A) Pressure builds up, causing the outer layers to expand until they are transparent enough for the energy to escape.
B) The star builds up so much energy that it explodes as a supernova.
C) The entire star heats up dramatically, causing the rate of fusion to increase in the core.
D) The star becomes a red giant.
A) Pressure builds up, causing the outer layers to expand until they are transparent enough for the energy to escape.
You might also like to view...
Why is Io's orbit about Jupiter slightly elliptical?
A) because of tidal forces due to Jupiter B) because Io was captured C) because of orbital resonances with the other three Galilean moons D) because of a giant impact which occurred in the past
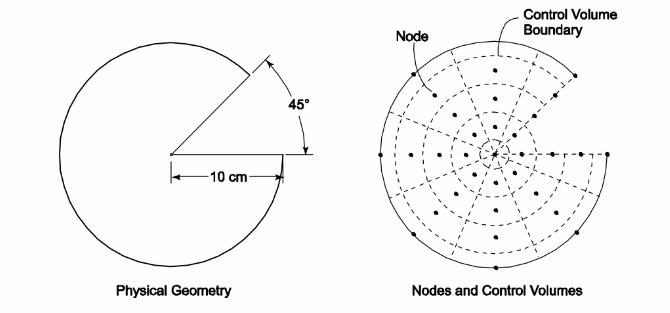
For the geometry shown in the sketch below, determine the layout of nodes and control volumes. Provide a scale drawing showing the problem geometry overlaid with the nodes and control volumes. Explain how to derive the energy balance equation for all the boundary control volumes.
GIVEN
Cylindrical geometry shown in the figure.
FIND
(a) A reasonable layout of nodes and control volumes
SKETCH
Nuclear Binding Energy: The stability of  Cl with respect to alpha, beta-plus and beta-minus decay is to be determined. The following atomic masses are known:
Cl with respect to alpha, beta-plus and beta-minus decay is to be determined. The following atomic masses are known:
A. not subject to alpha, beta-plus or beta-minus decay. B. subject to alpha decay only. C. subject to beta-plus decay only. D. subject to beta-minus decay only. E. subject to beta-plus or beta-minus decay, but not to alpha decay.
A spaceship is traveling to the moon. At what point is it beyond the pull of Earth's gravity?
A) when it is closer to the moon than it is to Earth B) when it gets above the atmosphere C) when it is half-way there D) when it is three-fourths of the way there E) It is never beyond the pull of Earth's gravity.