What is the power output of the turbine?
Steam at 200(psia) and 600(°F) [state 1] enters a turbine through a 3-inch-diameter pipe with a velocity of 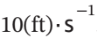 . The exhaust from the turbine is carried through a 10-inch-diameter pipe and is at 5(psia) and 200(°F) [state 2].
. The exhaust from the turbine is carried through a 10-inch-diameter pipe and is at 5(psia) and 200(°F) [state 2].
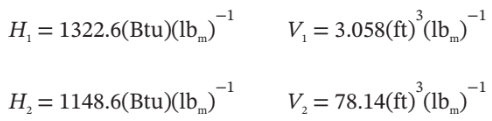
The volumetric flow rate into the pipe is the velocity 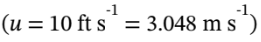 times the cross-sectional area
times the cross-sectional area 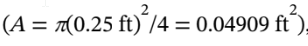 so the volumetric flowrate is
so the volumetric flowrate is 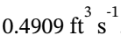 . Because the specific volume at these conditions is
. Because the specific volume at these conditions is 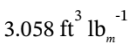 , the mass flowrate in is
, the mass flowrate in is 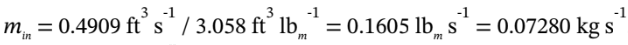 . At steady-state, the mass flow rate out must be the same as the mass flowrate in. So, if the specific volume at the outlet conditions is
. At steady-state, the mass flow rate out must be the same as the mass flowrate in. So, if the specific volume at the outlet conditions is 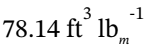 , then the volumetric flowrate out is
, then the volumetric flowrate out is 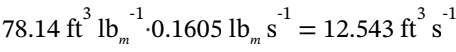 The cross-sectional area of the 10-inch diameter exit pipe is
The cross-sectional area of the 10-inch diameter exit pipe is 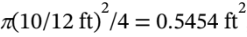 , so the velocity is
, so the velocity is 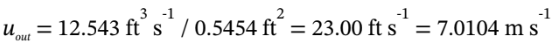 . Now, we can use this in the energy balance for an open
. Now, we can use this in the energy balance for an open
system.
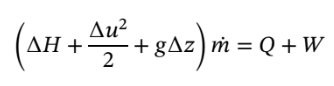
We will assume that the heat loss from the turbine is negligible (Q = 0) and that the change in elevation from inlet to outlet is negligible (?z = 0), so the work output of the turbine is given by:

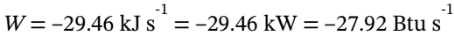 Our sign convention for W is that it is work done on the fluid, so the work output from the system is
Our sign convention for W is that it is work done on the fluid, so the work output from the system is 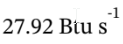 = 39.5 hp.
= 39.5 hp.
You might also like to view...
A college math department consisting of 10 faculty members must choose a department head, an assistant department head, and a faculty senate representative. In how many ways can this be done?
What will be an ideal response?
Why is the junction N between the two secondary coils usually grounded?
What will be an ideal response?
All safety glasses should meet standards set by ________
A MOD-8 asynchronous counter has a "worst case" propagation delay of tphl = 37 ns. The maximum input clock frequency for this counter would be:
A) 5.405 MHz B) 13.514 MHz C) 9.009 MHz D) 6.756 MHz