The marginal product of capital is the increase in
A) capital needed to produce one more unit of output.
B) output from a one-unit increase in capital.
C) labor needed to accompany a one-unit increase in capital.
D) output from a one-dollar increase in capital.
B
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as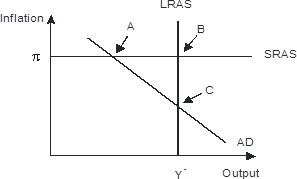
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
If you believe that the economy can achieve full employment without inflation through tax reductions, spending cuts, and deregulation, you are a member in good standing in the
a. classical school b. Keynesian school c. neo-Keynesian school d. rational expectations school e. supply-side school
If a machine cost $50,000 initially and is expected to last for 20 years but is worth $60,000 after one year because it is in short supply, an economist most likely would say that:
A. the value of the machine will continue to increase 20 percent per year for the next 20 years. B. during the first year the machine had no cost; it provides an implicit revenue of $10,000 to the firm. C. the machine's cost for each of its 20 years of existence is $3,000. D. the machine's cost for each of its 20 years of existence is $2,500.
Because consumption is largely determined by ________ income, consumption is ________ equally distributed than current income.
a. permanent, more b. permanent, less c. transitory, less d. transitory, more