Graphically illustrate the quantity rule and the shutdown rule for a price-taking firm.
What will be an ideal response?
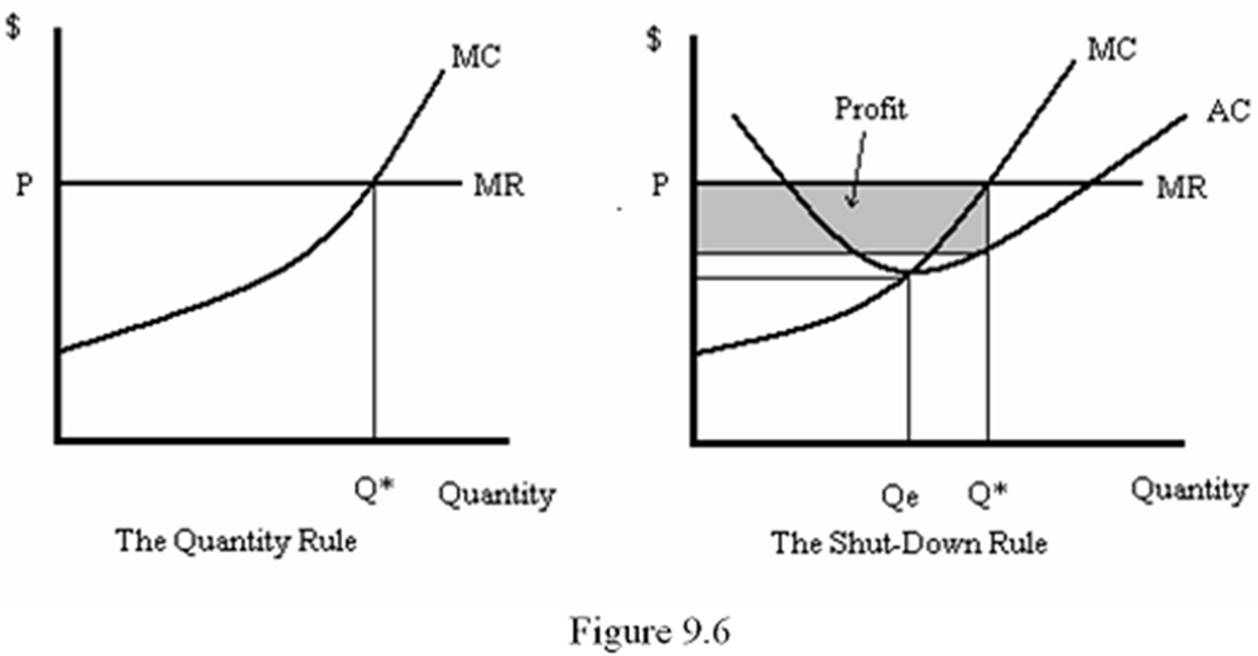
The most profitable level of output (Q*) occurs where P (= MR) = MC. This is illustrated in the left-hand panel of Figure 9.6 To apply the shutdown rule, check whether the profit from producing Q* is greater than the profit if the firm shuts down. This is done by comparing P to AC at the output level Q*. As seen in the right-hand panel of Figure 9.6 P is greater than AC at Q*. The firm's profits are shown by the shaded area. For a price-taking firm without sunk cost, any price below ACmin will cause the firm to shut down.
You might also like to view...
The price of soft drinks increases. Which of the following is not part of the likely chain of events that follows from this price change?
A. The demand for fruit juices increases. B. The manufacturers of soda?canning machines lay off some workers. C. Producers of soft drinks increase their production of soft drinks. D. Some consumers of soft drinks reduce their consumption of soft drinks.
In third-degree price discrimination, markets with a smaller price elasticity of demand are ________ responsive to price changes and are charged ________ prices than markets with a larger price elasticity of demand.
A) less; lower B) more; lower C) less; higher D) more; higher
From 1929 to 1933, U.S. output dropped by about
a. 10 percent b. 20 percent c. 25 percent d. 50 percent e. 75 percent
A change in the reserve requirement affects:
A. The money multiplier and excess reserves. B. Excess reserves and the discount rate. C. The discount rate and the federal funds rate. D. The money multiplier and the federal funds rate.