An extremely light rod 1.00 m long has a 2.00-kg mass attached to one end and a 3.00-kg mass attached to the other
The system rotates at a constant angular speed about a fixed axis perpendicular to the rod that passes through the rod 30.0 cm from the end with the 3.00-kg mass attached. The kinetic energy of the system is measured to be 100.0 J.
(a) What is the moment of inertia of this system about the fixed axis?
(b) What is the angular speed (in revolutions per second) of this system?
What will be an ideal response?
Answer: (a) 1.25 kg ? m2 (b) 2.01 rev/s
You might also like to view...
A possible means for making an airplane radar-invisible is to coat the plane with an antireflective polymer. If radar waves have a wavelength of 3.84 cm, and the index of refraction of the polymer is n = 1.6, how thick would the coating be if a 180° phase change occurs at both surfaces?
a. 24 mm c. 32 mm b. 7.5 mm d. 6.0 mm
The diagram illustrates a light source, a gas cloud, and three different lines of sight. Along which line of sight would an observer see an absorption spectrum?
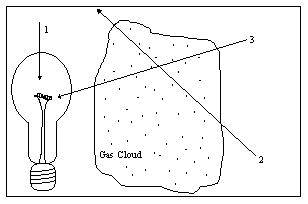
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 2 and 3
e. none of them
The fact that many radio lobes emit more intensely from the side away from the galaxy suggests that
a. they are formed by material falling into the galaxy. b. they are powered by magnetic fields. c. they are excited by radiation from nearby galaxies. d. they are powered by the rapid rotation of the galaxy. e. they are created by jets from the galaxy emitting where the material is halted.
Molecular clouds are mapped using CO instead of hydrogen because CO is much more abundant than hydrogen in molecular clouds
Indicate whether the statement is true or false