A flat-plate solar collector is used to heat water by having water flow through tubes attached at the back of the thin solar absorber plate. The absorber plate has a surface area of 2 m2 with emissivity and absorptivity of 0.9. The surface temperature of the absorber is 35°C, and solar radiation is incident on the absorber at 500?W/m2 with a surrounding temperature of 0°C. The convection heat transfer coefficient at the absorber surface is 5?W/m2•K, while the ambient temperature is 25°C. Net heat absorbed by the solar collector heats the water from an inlet temperature (Tin) to an outlet temperature (Tout). If the water flow rate is 5?g/s with a specific heat of 4.2?kJ/kg•K, determine the temperature rise of the water.
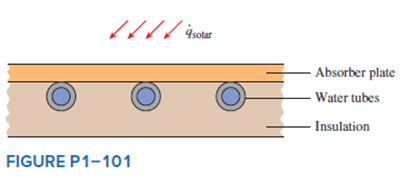
A flat-plate solar collector is used to heat water. The temperature rise of the water heated by the net heat rate from the solar collector is to be determined.
Assumptions 1 Steady operating conditions exist. 2 Specific heat of water is constant. 3 Temperature at the surface remained constant. 4 Conduction through the solar absorber is negligible. 5 Heat loss through the sides and back of the absorber is negligible.
Properties The absorber surface has an absorptivity of 0.9 and an emissivity of 0.9. The specific heat of water is given as 4.2 kJ/kg?K.
Analysis The net heat rate absorbed by the solar collector is
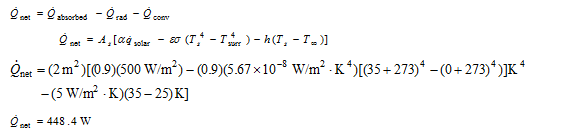
The temperature rise can be determined using
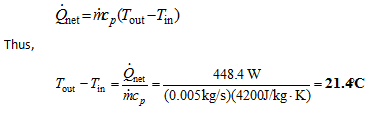
Discussion The temperature rise of the water is influenced by the usable net heat rate absorbed by the solar collector and the water flow rate.
You might also like to view...
The ____________________ establishes the goal for a number of departments, so if the drawing is vague, the entire organization is less efficient.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Modern ____________________ bridge designs are capable of spanning the greatest distance of all bridge designs.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
A molecule is:
A) Composed of photons and protons. B) Composed of protons and neutrinos. C) The smallest parts of an atom. D) The smallest part of a substance that is not an element.
Which of the following describes the consequence of noncondensable gases collecting in the condenser and the resulting increases in refrigerant temperature and pressure?
A) A reduction of system capacity and an increase in energy usage B) A freeze-up at the expansion valve or metering device C) The corrosion of metals throughout the system D) An increase in the efficiency of the refrigeration system