Using aggregate demand and aggregate supply analysis, explain why increases in oil did not lead to stagflation in 2006-2008 but did lead to stagflation in the 1970s and early 1980s
In the 1970s the increases in oil prices caused a decrease in aggregate supply which led to both higher prices and reduced output which is the very definition of stagflation. In contrast, the increased energy costs in the mid-2000 . did not shift aggregate supply inward ? at least not to the same degree. The reason is that the U.S. economy and other economies were no longer as dependent on energy with the energy content of U.S. GDP declining by 50%. In addition, sound economic policies and various structural changes made the economy less volatile since the 1980s which resulted in less severe movements in aggregate supply.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below.________ inflation will eventually move the economy pictured in the diagram from short-run equilibrium at point ________ to long-run equilibrium at point ________. 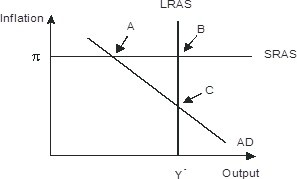
A. Rising; A B. Falling; A; C C. Falling; B: C D. Rising; A; C
Jane is a 25 year old, full-time student. She works part time in her school library and is paid $7 an hour. She is considered to be
A) not in labor force. B) not in the working-age population because she is in college. C) employed. D) unemployed. E) in labor force but not working.
Business taxes fall. This raises __________, which raises __________ and the __________ curve shifts rightward
A) consumption; aggregate demand (AD); AD B) investment; government purchases; AD C) investment; aggregate demand (AD); AD D) net exports; aggregate demand (AD); AD E) none of the above
The time value of the option should:
A. approach infinity at expiration. B. increase the longer the time to expiration. C. decrease the longer the time to expiration. D. not change with time to expiration.