Assume that foreign capital flows from a nation increase due to political uncertainly and increased risk. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a fixed exchange rate system, what happens to the GDP Price Index and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balance in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. The GDP Price Index falls and net nonreserve
international borrowing/lending balance becomes more negative (or less positive).
b. The GDP Price Index rises and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balance becomes more negative (or less positive).
c. The GDP Price Index falls and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balance becomes more positive (or less negative).
d. The GDP Price Index and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balance remain the same.
e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
.A
You might also like to view...
On-the-job training is the one area of education in the United States most influenced by the
a. business sector. b. government sector. c. household sector. d. foreign sector.
A consequence of a publicly owned natural monopoly is:
A. reduced chance to remain open longer than political terms of office. B. an increase in the motivation to improve efficiency. C. the loss of the profit motive. D. increased public pressure to reduce costs.
Which of the following is true of a common market?
A. There is free movement of capital and labor among the member countries. B. The member countries export similar products to the non-member countries. C. The member countries do not import goods from the non-member countries. D. The member countries have identical monetary and fiscal policies.
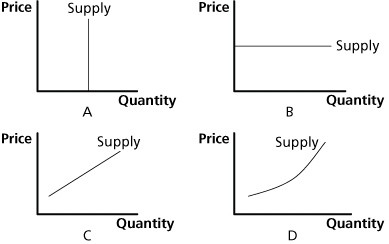
 In Figure 4.4, supply is perfectly elastic in graph:
In Figure 4.4, supply is perfectly elastic in graph:
A. A. B. B. C. C. D. D.