Distinguish between discretionary monetary policy and monetary “rules.” How do the mainstream economists and monetarists differ on their recommendations for the use of rules or discretionary policy?
What will be an ideal response?
Discretionary monetary policy is the use of an expansionary monetary policy to combat a recession and a contraction policy to combat an inflationary period. In other words, it is an activist monetary policy for stabilizing the economy. Mainstream economists would argue for discretionary monetary policy to complement fiscal stabilization policy. Monetarists argue for monetary “rules” designed to be implemented without regard to the state of the economy. Supposedly they will have a neutral effect on the cyclical ups and downs of the economy. A suggested monetary rule is to keep the money supply expanding at about 3 to 5 percent per year which is about the same as the potential growth rate of real GDP. The point for a monetary rule is to avoid mistakes and to provide enough liquidity to allow the economy to expand at its potential rate.
You might also like to view...
Use the following graph to answer the question below.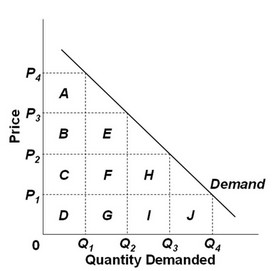 If the price is P3, then the total revenue is represented by area
If the price is P3, then the total revenue is represented by area
A. E + F + G. B. B + C + D + E + F + G. C. B + C + D. D. A + B + C + D + E + F + G.
A manager of a clothing firm is deciding whether to add another factory in addition to one already in production. The manager would compare a. The total revenue gained from the two factories to the total costs of running the two factories
b. The marginal revenue expected from the second factory to the total costs of running the two factories. c. The marginal revenue expected from the second factory to the marginal cost of the second factory. d. The total revenue gained from the two factories to the marginal costs of running the two factories.
Which of the following is correct? When actual leakages exceeds expected injections, then:
a. Inventories rise, unemployment tends to rise, and prices tend to fall. b. Inventories rise, unemployment tends to fall, and prices tend to rise. c. Inventories fall, unemployment tends to rise, and prices tend to rise. d. It is impossible for these two to be unequal. e. You are mixing apples and oranges. These two macroeconomic variables should not be compared.
A firm's average fixed cost is equal to the firm's:
A. fixed cost divided by its level of output. B. marginal cost divided by its level of output. C. fixed cost divided by its total revenue. D. level of output divided by its variable cost.