Using Figure 11.2, match the following:
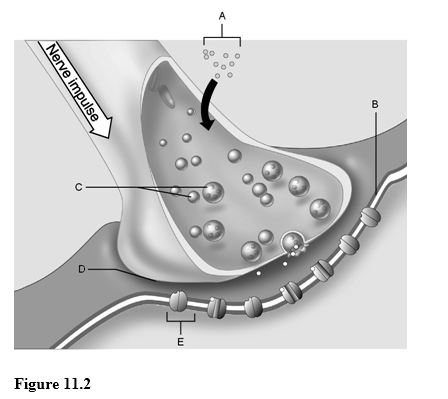
1) Ion channel.
2) Synaptic vesicles.
3) Calcium ions.
4) Postsynaptic membrane.
5) Synaptic cleft.
1) E
2) C
3) A
4) B
5) D
You might also like to view...
The system responsible for the exchange of gases between the blood and atmospheric air is the ________ system.
A. endocrine B. cardiovascular C. urinary D. nervous E. respiratory
A patient presents in the emergency department after he's been in a car accident. Because the patient is complaining about severe headaches, you suspect localized bleeding in his cranium. Moreover, you run tests and notice major swelling in this area. Which course of action should be a priority?
A. Inducing local vasodilation B. Increasing pressure in the area to decrease bleeding C. Decreasing inflammation to prevent tissue damage D. Increasing the temperature in the cranial area to induce a fever
Functions of the large intestine include
A) storage of fecal material prior to defection. B) absorption of vitamins. C) reabsorption of water and compaction of feces. D) All of the answers are correct. E) None of the answers is correct.
An EPSP:
A. is a direct result of the opening of ligand-gated channels permeable to both Na+ and K+ ions. B. is a direct result of the opening of voltage-gated channels permeable to both Na+ and K+ ions. C. stabilizes the membrane to remain at its resting potential. D. opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in the presynaptic membrane. E. occurs when voltage-gated Cl- channels open in a postsynaptic cell membrane.