You are dispatched to a recreational vehicle (RV) park for an unconscious patient. When you arrive at the scene, another resident of the park tells you that the patient, a young man, is in his RV and will not answer the door. After safely entering the RV, you find the patient lying supine near the rear of the vehicle. From a distance, you can tell that he is not breathing. As you approach him, you see several bottles of Sudafed, a container of camping fuel, and a variety of glass containers with an unknown liquid in them. What should you do?
A) Realize that you are in a methamphetamine drug lab, immediately exit the RV, and notify law enforcement personnel.
B) Suspect that the patient has ingested a variety of harmful chemicals, begin CPR, and request a backup team of paramedics.
C) Quickly remove the patient from the vehicle if it is safe to do so, begin CPR away from the RV, and ask the resident to call the police.
D) Assess for a carotid pulse, perform CPR for 2 minutes, assess the patient's cardiac rhythm, and defibrillate one time if he is in a shockable rhythm.
Answer: C) Quickly remove the patient from the vehicle if it is safe to do so, begin CPR away from the RV, and ask the resident to call the police.
You might also like to view...
The controller’s approach to conflict is to:
What will be an ideal response?
Which of these conditions or diseases is caused by a virus?
A. Vaginitis B. Lice C. Lyme disease D. Genital herpes
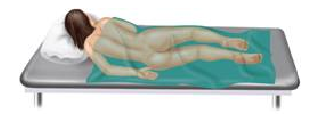
The examination position pictured here is the ________ position.
Proper placement of the electrode sensors is imperative to ensure accuracy.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)