Velocities have both direction and magnitude and thus are vectors. The magnitude of a velocity vector is called speed. Suppose that a wind is blowing from the direction N 60° W at a speed of 80 km/h. (This means that the direction from which the wind blows is 60° west of the northerly direction.) A pilot is steering a plane in the direction N 45° E at an airspeed (speed in still air) of 250 km/h. The true course, or track, of the plane is the direction of the resultant of the velocity vectors of the plane and the wind. The ground speed of the plane is the magnitude of the resultant. Find the ground speed of the plane. Round the result to the nearest hundredth.
What will be an ideal response?
281.51
Mathematics
You might also like to view...
One of the benefits of the functional structure is that its elements are the same across different business-level strategies.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Mathematics
Find a rectangular-coordinate equation for the curve by eliminating the parameter.  figure 1.png)
 figure 2.png)
Mathematics
Determine the solution set of the inequality from the given graph.x2 + 4x < 2x + 8 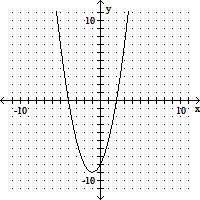 x-intercepts: (-4, 0), (2, 0)
x-intercepts: (-4, 0), (2, 0)
A. (-4, 2) B. [-4, 2] C. (-?, -4) ? (2, ?) D. (2, 4)
Mathematics
Find the exact function value if it exists.csc (-630°)
A. 0 B. Undefined C. 1 D. 2
Mathematics