Refer to the normal-form game of price competition shown below. 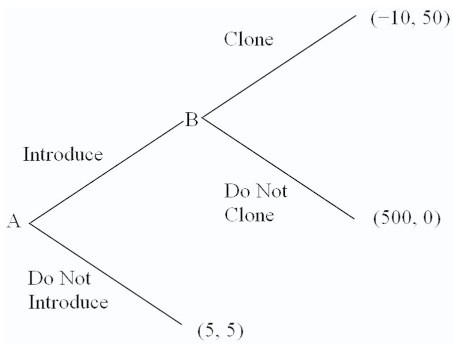 Firm A must decide whether or not to introduce a new product. If firm A introduces a new product, firm B must decide whether or not to clone the product. The payoff structure of the game is depicted in Figure 10-12. The subgame perfect Nash equilibrium to this game is:
Firm A must decide whether or not to introduce a new product. If firm A introduces a new product, firm B must decide whether or not to clone the product. The payoff structure of the game is depicted in Figure 10-12. The subgame perfect Nash equilibrium to this game is:
A. Firm A plays "Do Not Introduce"; firm B plays "Clone" if firm A plays "Introduce."
B. Firm A plays "Introduce"; firm B plays "Clone" if firm A plays "Introduce."
C. Firm A plays "Introduce"; firm B plays "Do Not Clone" if firm A plays "Introduce."
D. Firm A plays "Do Not Introduce"; firm B plays "Do Not Clone" if firm A plays "Introduce."
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
If aggregate demand is stable and there is economic growth, the economy will experience
A) secular depreciation. B) secular decline. C) secular deflation. D) secular degeneration.
Part-time workers are considered both a part of the labor force and employed
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Cigarettes are highly addictive and therefore have a very low elasticity of demand. A $2.00 increase in the national sales tax on cigarettes would likely cause the price paid by buyers of cigarettes to
A) increase by more than $1.00 but less than $2.00. B) increase by $2.00. C) increase by more than $2.00. D) increase by less than $1.00. E) remain unchanged.
At the point of maximum profit, marginal revenue equals
a. variable cost. b. fixed cost. c. average total cost. d. marginal cost.