Define the following terms and explain their importance to the study of macroeconomics:
a. money
b. M1
c. near money
d. bank run
a. Money is the standard object used in the exchange of goods and services. Therefore, money serves as the medium of exchange. Changing the amount of money in circulation is a tool of macroeconomics, because money is a major determinant of aggregate demand.
b. M1 is the narrowest definition of the money supply. It is the sum of all coins and paper currency in circulation, conventional checking accounts, travelers' checks, and checkable deposits at banks and savings institutions. It consists of the most liquid (spendable) financial assets that can be used to make payments.
c. Near money is a liquid asset that is a close substitute for money. However, it is not nearly as spendable as the items in M1 . Some near monies include savings accounts and money market deposit accounts.
d. A bank run occurs when many bank depositors attempt to withdraw their funds all at once. This can pose a danger for banks in a fractional reserve system, because a bank usually does not have sufficient cash on hand to meet demands for withdrawals from all accounts.
You might also like to view...
Institutions that channel funds from suppliers of financial capital to users of financial capital are referred to as:
A) deposit insurance committees. B) financial intermediaries. C) central banks. D) mutual funds.
Does U.S. Steel prefer to own coal mines? Give reason for your answer
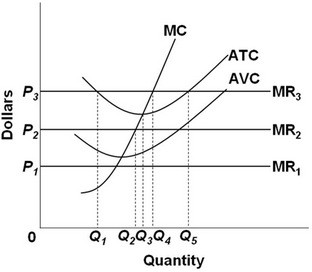 Refer to the above diagram. All data are for the short run. The firm represented in this diagram is selling under conditions of:
Refer to the above diagram. All data are for the short run. The firm represented in this diagram is selling under conditions of:
A. pure competition. B. pure monopoly. C. oligopoly. D. monopolistic competition.
Suppose that the profit maximizing level of output for the monopolist is 100 units, and ATC = $45.00; MC = $35.00; MR = $35.00; P = $60.00. What is the monopoly's profit?
A. $1500 B. -$1000 C. $5000 D. $4500