Using Map T-22b, the “SP Mountain, Arizona,” quadrangle (scale 1:24,000; contour interval 40 feet), calculate the gradient of SP Mountain (35°34'56"N, 111°37'55"W) from the north base of the cone (at the 6200' contour) toward the crater rim. On the edge of a piece of paper measure out a distance of 0.2 miles using the graphic map scale, and then determine the elevation change over that distance.
In this problem, you will compute the gradients of Mauna Loa in Hawai‘i, Mount Vsevidof in Alaska, and SP Mountain in Arizona. (You may also determine the elevation changes and distances needed to calculate these gradients by using Google Earth™.) The recommended starting point and distance to measure are given for all three volcanoes.
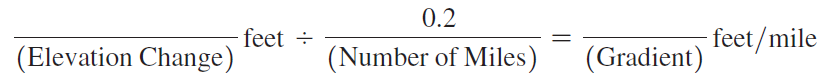
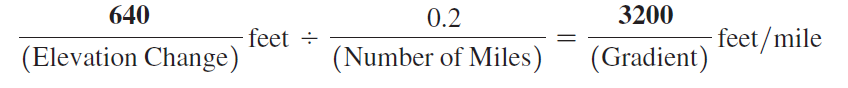
You might also like to view...
Matter is anything that
A. has mass and takes up space. B. has the capacity to do work. C. can be changed in form. D. can produce change. E. moves mass.
Streams with broad, shallow channels and narrow, deep channels have a higher flow velocity than do
those with semi-circular channels Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
Choose the answer that best explains why a rock might not go through the complete rock cycle.
A. Rock may be involved in a variety of processes in different sequences. B. The exposed rock may never weather thus never enter the rock cycle again. C. Some rocks are forever trapped in the magma of the Earth.
The ________ led to decreases in agricultural productivity in Renaissance Europe
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).