The aggregate supply-aggregate demand model suggests that the government can stabilize an economy that experiences a sudden and unexpected decline in consumer confidence and aggregate demand by:
What will be an ideal response?
Increasing the money supply.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is true of a beneficial supply shock? a. It can lead to a temporary lower price level
b. It can create a recessionary gap. c. It can permanently decrease the economy's price level. d. It can shift the aggregate demand curve rightward. e. It can shift the aggregate demand curve leftward.
The coordination task of dividing products among consumers is a problem of
a. output selection. b. production planning. c. distribution. d. market segmentation.
The price that a person must pay in order acquire purchasing power now rather than in the future is called
a. the interest rate. b. the foreign exchange rate. c. the inflationary premium. d. the risk premium.
In the Aggregate Demand - Aggregate Supply diagram in Figure 8.1, Box 2 should be filled with 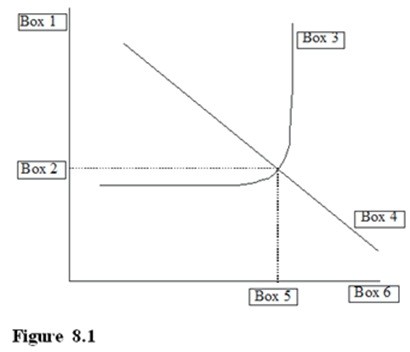
A. AD for Aggregate Demand. B. AS for Aggregate Supply. C. PI* for macroeconomic equilibrium Price Index. D. RGDP* for macroeconomic equilibrium Real Gross Domestic Product.