If a length of lucite that is being used as a light pipe gets wet, the critical angle
A)
decreases.
B)
is unaffected.
C)
doubles.
D)
is meaningless since lucite cannot be used as a light pipe.
E)
increases.
A
You might also like to view...
At a pressure of 1 atmosphere, a mixture of two metals (A and B) has the three phases ?, ?, and ? in equilibrium. Can the temperature be changed and still have the ?, ?, and ? phases in equilibrium? _____________
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
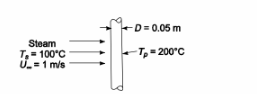
Replot the data points of Figure 5.9(b) on log-log paper and find an equation approximating the best correlation line. Compare your results with Figure 5.10. Then, suppose that steam at 1 atm and 100°C is flowing across a 5-cm-OD pipe at a velocity of 1 m/s. Using the data in Figure 5.10, estimate the Nusselt number, the heat transfer coefficient, and the rate of heat transfer per meter length of pipe if the pipe is at 200°C and compare with predictions from your correlation equation.
GIVEN
Figure 5.9(b) in text
Steam flowing across a pipe
Steam pressure = 1 atm
Steam temperature (Ts) = 100°C
Pipe outside diameter (D) = 5 cm = 0.05 m
Steam velocity (U?) = 1 m/s
Pipe temperature (Tp) = 200°C
FIND
(a) Replot Figure 5.9(b) on log-log paper and find an equation approximating the best correlation line
(b) Find the Nusselt number (Nu), the heat transfer coefficient (hc), and the rate of heat transfer per
unit length (q/L) using Figure 5.10
(c) Compare results with your correlated equation
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady state
Radiative heat transfer is negligible
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
From Appendix 2, Table 35, for steam at 1 atm and 100°C
Coulomb's Law: As shown in the figure, charge q1 = 2.2 × 10-6 C is placed at the origin and charge q2 = -3.30 × 10-6 C is placed on the x-axis, at x = -0.200 m. Where along the x-axis can a third charge Q = -8.30 × 10-6 C be placed so that the resultant force on Q is zero?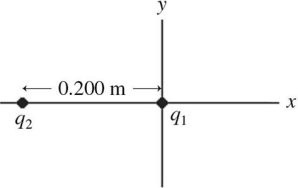
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
A force is non-conservative if the net work done by the force on an object moving around any closed path is zero
Indicate whether the statement is true or false