(a) Plot the grain-size distribution curve for this sample. (b) Determine D10, D30, and D60. (c) Calculate the uniformity coefficient, Cu. (d) Calculate the coefficient of gradation, Cc.
Following are the results of a sieve analysis:
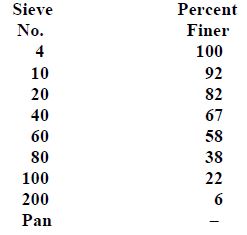
What will be an ideal response?
(a) Grain-size distribution are shown as follows,
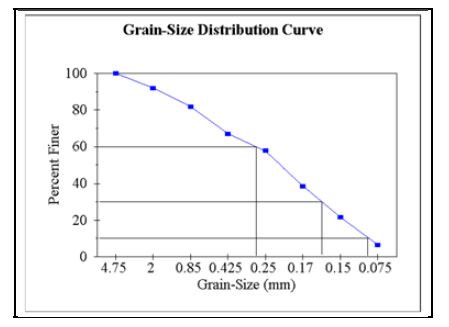
(b) From the preceding figure, D10 = 0.100 mm
D30 = 0.160 mm
D60 = 0.279 mm
(c) The coefficient of uniformity can be calculated using Equation 17.19:
Cu = (D60 / D10)
Cu = 0.279 / 0.100
Cu = 2.79
(d) The coefficient of curvature can be calculated using Equation 17.20:
Cc = D302 / (D60)(D10)
Cc = (0.160)2 / (0.279)(0.100)
Cc = 0.92
You might also like to view...
Explain why field-fabricated air chambers are not as effective for water hammer protection as mechanical arrestors.
What will be an ideal response?
The maximum force a material can withstand is called its ____________________ strength.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
The sulfur dioxide in the atmosphere ________
A) can be an important source of sulfur nutrition for plants B) comes from fires such as fossil fuel burning, volcanoes and forest fires C) is a major contributor to "acid rain" D) all of the above E) none of the above
The ring around the 6GR all-position pipe is there to ________ the operation
A) Restrict B) Balance C) Hold heat for D) Improve E) None of the above