If the aggregate demand curve shifts in the short run moving the economy out of long-run equilibrium:
A. the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to bring it back into long-run equilibrium.
B. the aggregate demand curve will eventually shift back once expectations are taken into account.
C. inflation will always occur.
D. we will move along the short-run aggregate supply curve back to equilibrium.
A. the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to bring it back into long-run equilibrium.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following pairs is the most likely to exhibit a direct relationship?
a. The price of gasoline and the amount of gasoline that people purchase. b. Cholesterol levels and the likelihood of developing heart disease. c. Outdoor temperature and heating oil sales. d. Annual income and weekly pawn shop visits.
When economists compare monopoly to the monopolistic competitive market, they show that the latter generates
a. fewer choices for consumers b. higher prices for consumers c. higher economic profit (the sum of the economic profit of all firms) d. less output because monopolies are more efficient e. lower prices for consumers
Which of the following will NOT cause increasing returns to scale and declining average costs?
a. focusing on a single product line and specializing b. exporting goods to other countries c. selling more in their home market d. hiring more workers at the existing plant
Refer to the graphs shown, which show indifference curve analysis with the associated demand curves.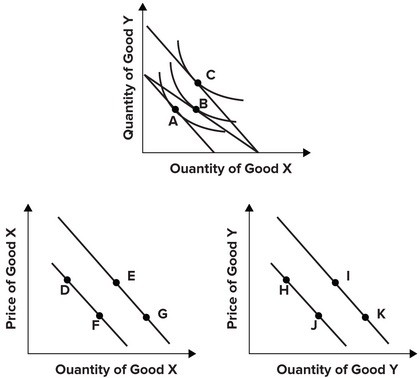 The best explanation for a movement from point D to point F is:
The best explanation for a movement from point D to point F is:
A. an inward rotation of the budget constraint along the x-axis, forcing the consumer to move from point B to point A. B. an outward rotation of the budget constraint along the x-axis, allowing the consumer to move from point A to point B. C. a parallel shift of the budget constraint, allowing the consumer to move from point A to point C. D. an outward rotation of the budget constraint along the y-axis, allowing the consumer to move from point B to point C.