Deadweight loss refers to
A) the opportunity cost to firms from producing the equilibrium quantity in a competitive market.
B) the sum of consumer and producer surplus.
C) the loss of economic surplus when the marginal benefit equals the marginal cost of the last unit produced.
D) the reduction in economic surplus resulting from not being in competitive equilibrium.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The term human capital refers to
A) labor resources used to make capital equipment. B) buildings and machinery. C) people's knowledge and skill. D) entrepreneurship and risk-taking.
An example of statistical discrimination would be:
A. charging young drivers a higher premium than older drivers. B. charging homes near a lake higher premiums for flood insurance than those on a hill. C. assuming the food will be better at an Italian restaurant than a Chinese one in the Little Italy neighborhood of NYC. D. All of these are examples of statistical discrimination.
In volatile markets, "speculators" would be expected to provide some stability because:
a. they will be required to do so by the government. b. they will use current price moves to predict future moves. c. they will buy when price is below equilibrium and sell when it is above equilibrium. d. they will buy when price is above equilibrium and sell when it is below equilibrium.
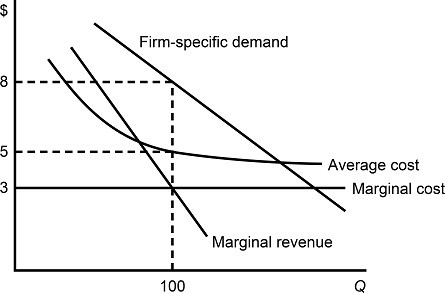
 Figure 8.4 depicts demand and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. If the firm's demand curve shifts to the left as more firms enter the market:
Figure 8.4 depicts demand and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. If the firm's demand curve shifts to the left as more firms enter the market:
A. the firm's average cost will be lower at the new profit-maximizing output level. B. the firm's marginal cost will be higher at the new profit-maximizing output level. C. the firm's marginal revenue will remain the same at the new profit-maximizing output level. D. the firm's marginal cost will remain the same at the new profit-maximizing output level.