Charge of uniform density (80 nC/m3) is distributed throughout a hollow cylindrical region formed by two coaxial cylindrical surfaces of radii 1.0 mm and 3.0 mm. Determine the magnitude of the electric field at a point which is 4.0 mm from the symmetry axis.
A. 7.9 N/C
B. 10 N/C
C. 9.0 N/C
D. 8.9 N/C
E. 17 N/C
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
In the shear mode II of fracture, the crack propagates _________to the forces that produce the shear stress.
What will be an ideal response?
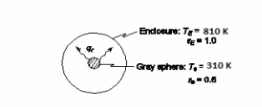
A small gray sphere having an emissivity of 0.5 and a surface temperature of 5370C is located in a blackbody enclosure having a temperature of 37°C. Calculate for this system: (a) the net rate of heat transfer by radiation per unit of surface area of the sphere, (b) the radiative thermal conductance in W/K if the surface area of the sphere is 95 cm2 , (c) the thermal resistance for radiation between the sphere and its surroundings, (d) the ratio of thermal resistance for radiation to thermal resistance for convection if the convective heat transfer coefficient between the sphere and its surroundings is 11 W/(m2 K), (e) the total rate of heat transfer from the sphere to the surroundings, and (f) the combined heat transfer coefficient for the sphere.
GIVEN
• Small gray sphere in a blackbody enclosure
• Sphere emissivity (?s) = 0.5
• Sphere surface temperature (T1) = 3370C= 810 K
• Enclosure temperature (T2) = 37°C = 310 K
• The surface area of the sphere (A) = 95 cm2=9.5*10-3 m2
• The convective transfer coefficient ( ch ) = 11 W/(m2 K)
FIND
(a) Rate of heat transfer by radiation per unit surface area (b) Radiative thermal conductance (Kr) in W/K (c) Thermal resistance for radiation (Rr) (d) Ratio of the radiative and conductive resistance (e) Total rate of heat transfer (qT) to the surroundings (f) Combined heat transfer coefficient ( cr h )
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state prevails
• The temperature of the fluid in the enclosure is equal to the enclosure temperature
SKETCH
What is proper motion?
A) It is the true, not apparent, motion of a star in space. B) It is the apparent shift as we go to opposite sides of our orbit every six months. C) It is the annual apparent motion of a star across the sky. D) It is the motion of a star towards or away from us, revealed by Doppler shifts. E) It is the orbital motion of a star around the Galaxy.
On average, how often do impacts large enough to produce mass extinction on the Earth occur?
A) once every century B) once every million years C) once in Earth's history D) once every thousand years E) once every hundred million years