When a monopolist sells the same product at different prices and the prices are NOT related to cost differences, we have
A) monopoly pricing.
B) marginal cost pricing.
C) price discrimination.
D) price differentiation.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Because financial markets clear, we know that leakages in the economy will equal injections and, therefore, there will be enough spending in the economy to purchase whatever amount of output level produced
a. True b. False
An efficient distribution of goods requires that
a. everyone gets an equal share of each good. b. marginal cost equal marginal utility for the last unit produced. c. each person derives the same total utility from the good. d. since tastes differ, every person pays a different price in accordance with different marginal utilities.
To answer the question, refer to the following table showing a demand schedule: 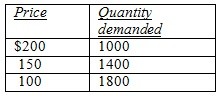 If price falls from $200 to $150,
If price falls from $200 to $150,
A. an arrow representing the price effect points down and is longer than an arrow for the quantity effect. B. an arrow representing the quantity effect points up and is shorter than an arrow for the price effect. C. arrows representing the price and quantity effects both point down. D. total revenue moves in the same direction as the arrow representing the quantity effect. E. arrows representing the price and quantity effects both point up.
Monetary policy actions are determined by the
A. President of the United States. B. New York Federal Reserve Bank. C. Federal Open Market Committee. D. all of these