What are the implications of a liquidity trap for the Federal Reserve?
What will be an ideal response?
The Fed can add liquidity to the bank system by increasing its excess reserves, but that does not mean that banks will want to lend money. If banks do not lend, then there will not be the increase in consumer spending and increase in business investment that will help increase aggregate demand. The liquidity trap occurs because banks are reluctant to lend to businesses, households, and other financial institutions when they are uncertain about the future and are concerned about whether loans will be repaid. Thus the available liquid to help stimulate the economy remains trapped as excess reserves held at the Federal Reserve banks.
You might also like to view...
The U.S. economy has had persistent inflation in recent decades. A possible explanation for the inflation is that
A) there have been decreases in the growth rate while aggregate demand has remained unchanged. B) growth in aggregate demand has been greater than growth in aggregate supply. C) there have been decreases in aggregate demand while aggregate supply has remained unchanged. D) there have been increases in the growth rate while aggregate demand has remained unchanged.
Using demand and supply analysis, explain why the euro/dollar exchange rate rises (the dollar appreciates) if the Fed intervenes in the foreign exchange market and sells euros.
What will be an ideal response?
Movement from q1 to q* will cause which of the following to happen?
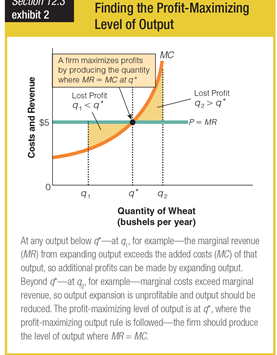
a. a decrease in profits
b. an increase in profits
c. a leveling off of profits
d. a fluctuation in profits
Social Security is
A. a social insurance program that guarantees that an elderly person will never fall below the poverty level. B. an insurance program operated by the federal government. C. a retirement program that invests the person's contributions into interest-earning financial assets so the proceeds can fund the person's retirement. D. an intergenerational transfer program that only vaguely relates to past earnings.