The profit-maximizing price and quantity of the monopolist compared to the perfectly competitive industry in the above figure are, respectively
A) A and B.
B) A and C.
C) A and F.
D) C and F.
C
You might also like to view...
Why does perfect competition shun advertising? Does advertising benefit a monopoly?
What will be an ideal response?
The move to an international gold standard between 1896 and World War I:
a. encouraged the free flow of goods and capital between countries. b. was accompanied by moderate increases in prices. c. required a higher use of resources than would have been the case under a paper standard. d. made it difficult to exercise expansionary monetary policy. e. All of the above.
According to the graph shown, if the economy is operating in autarky and decides to open trade with a tariff, the impact on domestic demand is they will:
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good, as well as a tariff and the world price for that good.
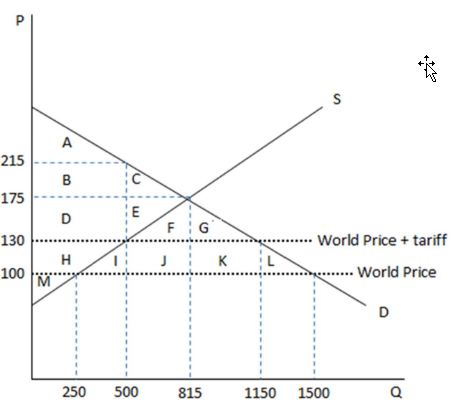
A. decrease consumption from 1500 to 1150.
B. increase consumption from 815 to 1500.
C. increase consumption from 815 to 1150.
D. decrease consumption from 1500 to 815.
A positive externality is:
A. an external benefit. B. an external cost that affects the buyer. C. an external cost that affects the seller. D. a benefit that affects the buyer, not the seller.