What is the behavior of the Ekman spiral? What occurs when the friction depth is reached? What will be an ideal response?
ANS:Answer
should include:
? Water moves at a 45? angle from the wind direction. It moves to the right in the
Northern Hemisphere and left in the Southern Hemisphere. With each deep layer of
water, the angle of movement continues in relation to the floe in the layer above it. Each
layer, however, moves slower than the layer above it. This is the Ekman spiral.
? The deflection of the current movements is due to the Coriolis Effect. It shifts the
direction of the topmost layer. The other layers then move in response to that initial
layer.
? At a certain depth in the Ekman spiral the water flows in the opposite direction of the
surface current. This is called the friction depth.
? The net movement of water directions in the Ekman spiral is called the Ekman transport.
This should travel approximately 90? angle of the wind direction, but it barely reaches a
45? deflection angle. This is the result of interactions between the Coriolis Effect and the
pressure gradient.
You might also like to view...
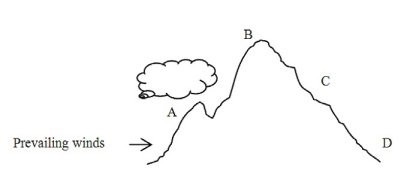 Air moving in the direction indicated in the diagram will become dryer as it moves from
Air moving in the direction indicated in the diagram will become dryer as it moves from
A. D to A B. B to D C. A to B D. C to A E. None of these is correct
In its evolutionary sense, fitness reflects the ability to respond to
A) other members of the same species with whom resources are shared. B) abiotic environmental factors such as drought, hurricanes and fires. C) develop a comprehensive survival strategy (niche) for maintaining a sustainable population. D) predators, parasites and other agents of disease.
Violet-colored light travels at the ________ rate and is therefore refracted the ________
A) fastest; least B) slowest; least C) fastest; most D) slowest; most
Car accidents have killed more Americans than all wars in the country's history.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)