Many plants are filled with toxins that kill or deter herbivores. Many plants sequester these compounds within the cell. Where in the plant cell are these toxic substances most likely stored?
A. Central vacuole
B. Mitochondria
C. The stroma
D. Amyloplasts
E. Lysosomes
Clarify Question
· What is the key concept addressed by the question?
· What type of thinking is required?
· What key words does the question contain and what do they mean?
Gather Content
· What do you already know about about plant toxin sequestration? How does it relate to the question?
Consider Possibilities
· What other information is related to the question? Which information is most useful?
Choose Answer
· Given what you now know, what information and/or problem solving approach is most likely to produce the correct answer?
Reflect on Process
· Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
A. Central vacuole
Clarify Question
· What is the key concept addressed by the question?
o This question is asking where toxins are stored in plants.
· What type of thinking is required?
o You are being asked to take what you already know and apply it to the understanding of where plants store toxins.
· What key words does the question contain and what do they mean?
o Herbivore, which refers to an organism that eats plants.
o Sequester, which means to store.
Gather Content
· What do you already know about about plant toxin sequestration? How does it relate to the question?
o Plants can store toxins in membrane-bound structures.
o The central vacuole of a plant is membrane-bound.
o The central vacuole of a plant cell is a storage area for many different molecules.
Consider Possibilities
· What other information is related to the question? Which information is most useful?
o Amyloplasts store starch.
o The stroma is not a membrane-bound organelle.
Choose Answer
· Given what you now know, what information and/or problem solving approach is most likely to produce the correct answer?
o Toxins are stored in membrane-bound structures with plant cells. The membrane-bound structure that is known for macromolecule storage is the central vacuole.
Reflect on Process
· Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
· Apply level:
o This question asked you to identify the location in which toxins are stored. Answering this question correctly depended on your ability to use your knowledge of plant cell structure and function in a new situation. If you got the correct answer, great job! If you got an incorrect answer, where did the process break down? Did you remember that the central vacuole is an area in which molecules are stored, or that toxins are stored in membrane-bound structures? Did you have trouble extending your knowledge of plant cell structure to determine the correct answer?
You might also like to view...
Look at the illustration and think about what you have learned about the regulation of the cell cycle. If Rb were mutated and could not be phosphorylated or bind E2F, which would be a possible outcome?
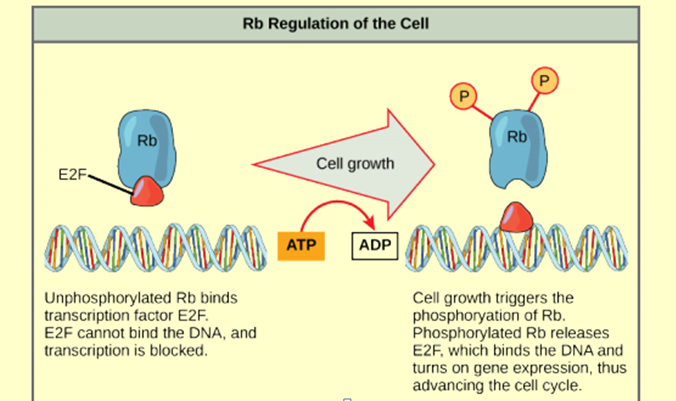
a. E2F would bind and transcription would proceed.
b. Rb would block transcription and apoptosis would be triggered.
c. Cancer would result due to unchecked cell growth and mitosis.
d. Transcription would be blocked and the cell cycle could not proceed.
What tissue in vascular plants would be used to move sugars from roots to the stems and leaves, and
from leaves to roots and stems?
a. sclerenchyma b. phloem c. collenchyma d. parenchyma e. xylem
Adaptations that evolved in the group of animals called the _____ have allowed them to complete their life cycles entirely on land
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Succession on sand dunes at the southern end of Lake Michigan and succession in nearby marshes share which of the following in common?
A) their early successional stages C) their climax communities B) their mid-successional stages D) none of the above