Process of Science: Explain the reasoning that led to our understanding of nuclear energy being the source of the Sun's light
What will be an ideal response?
The first step was measuring the distance to the Sun which then allowed us to calculate how luminous it is and therefore how much energy is needed to power it. The energy requirements are much larger than chemical reactions (i.e., fire) so this was then ruled out. A longer lived source that could match the energy requirements is gravitational contraction. However, as geologists and paleontologists found evidence for an ancient Earth, astronomers realized that gravitational collapse could not be the dominant energy source of our Sun today. All known energy sources were eliminated and only after the recognition that mass can be converted directly into energy, was the solution of the Sun's light as nuclear energy understood.
You might also like to view...
Solar One, located near Barstow, CA, was the first large-scale (10 MW electric) solar- thermal electric-power-generating plant in the United States. A schematic diagram of the plant is shown below. The receiver may be treated as a cylinder 7 m in diameter and 13.5-m-tall. At the design operating conditions, the average outer surface temperature of the receiver is about 675°C and ambient air temperature is about 40°C. Estimate the rate of heat loss, in MW, from the receiver—via natural convection only—for the temperatures given. What are other mechanisms by which heat may be lost from the receiver?
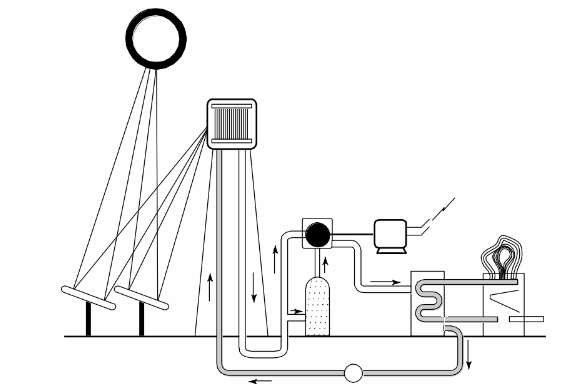
GIVEN
• A vertical cylinder in air
• Height of cylinder (L) = 13.5 m
• Diameter (D) = 7 m
• Surface temperature (Ts) = 675°C
• Ambient air temperature (T?) = 40°C
FIND
(a) The rate of convective heat loss (qc) in MW
(b) What other mechanisms for heat loss exist?
ASSUMPTIONS
• Air is still
• Surface temperature is uniform and constant
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at the mean temperature of 357.5°C
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.00160 1/K
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0461 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 58.1 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.72
The expansion of the universe is due to the
A) motion of galaxies through space B) expansion of space within galaxies C) expansion of stars within galaxies D) expansion of space between galaxies
A constant horizontal pull acts on a sled on a horizontal frictionless ice pond. The sled starts from rest. When the pull acts over a distance x, the sled acquires a speed v and a kinetic energy K
If the same pull instead acts over twice this distance: A) The sled's speed will be 2v and its kinetic energy will be 2K. B) The sled's speed will be 2v and its kinetic energy will be K . C) The sled's speed will be v and its kinetic energy will be 2K. D) The sled's speed will be v and its kinetic energy will be K . E) The sled's speed will be 4v and its kinetic energy will be 2K.
During the epoch of decoupling, nuclei and electrons combined to form atoms
Indicate whether the statement is true or false