Table 36-1Suppose the economy of Macroland is described by the following:C = 200 + 0.8 DI (DI = disposable income)I = 300 + 0.2Y?50r (Y = GDP)(r, the interest rate, is measured in percentage points. For example, a 9 percent interest rate is r = 9).For this economy, assume that the Federal Reserve uses its monetary policy to peg the interest rate atr = 5G = 750T = 0.25YX = 200M = 150 + 0.2YHint: DI = Y?T
From Table 36-1, compute equilibrium GDP for Macroland.
A. 3,000
B. 2,950
C. 2,625
D. 2,525
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Consider a consumer with a choice set that emerges from an exogenous income I. Suppose that, as a result of changes in a consumer's economic circumstances, the budget line rotates outward, with the vertical intercept remaining unchanged but the horizontal intercept shifting to the right. How could this have happened if the price of the good on the horizontal axis did not change?
What will be an ideal response?
In the long run, increases in output per person arise primarily from:
A. increases in female labor force participation. B. increases in average labor productivity. C. an increasing proportion of the population retiring D. increases in male labor force participation.
The current price per share of the XYZ company, which is traded on the New York Stock Exchange, is $100. At that price, the total quantity of shares demanded is 1,000 and the total quantity supplied for trade is 1,500. It follows that
a. $100 is the equilibrium price per share. b. there will be downward pressure on the price of shares of the XYZ company. c. there will be upward pressure on the price of shares of the XYZ company. d. there is a shortage of shares of the XYZ company on the stock exchange.
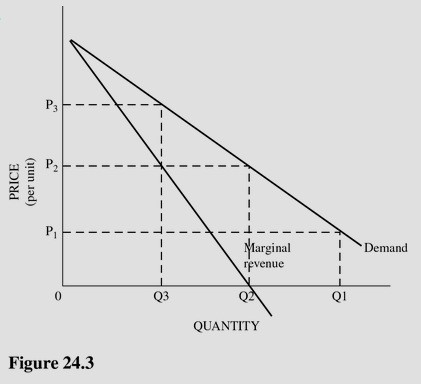 Refer to Figure 24.3. Suppose this good could somehow be produced at no cost (that is, the total cost at any level of output was zero). This single-price monopoly firm would maximize profit by
Refer to Figure 24.3. Suppose this good could somehow be produced at no cost (that is, the total cost at any level of output was zero). This single-price monopoly firm would maximize profit by
A. Raising the price as high as possible until the quantity demanded began to decrease. B. Producing Q3 and charging P3. C. Producing Q2 and charging P2. D. Producing an infinite amount and selling at the highest price possible.