Rebel Sole is a rapidly expanding shoe company. The following is the demand estimate for its popular shoes. The estimate was done using 40 observations.
Q = 10 -10 P + 4 A +0.42/+ 0.25Py (3) (1.8) (0.7) (0.1) (0.1)
F = 93, s = 6, R2 = 93%
Q is quantity sold (in thousands), P is shoe price, A is advertising expenditure (in thousands), the numbers in parentheses are standard errors. I is disposable income per capita (thousands of dollars), and Py is the price of related goods.
a. Evaluate the model based on F, R².
b. Test the significance of Py
c. If P=$5, A = $30,000, I = 50,000, and Py = $6, calculate advertising elasticity.
d. Given the information in c. above, calculate the 95% confidence interval for Q.
Answer:
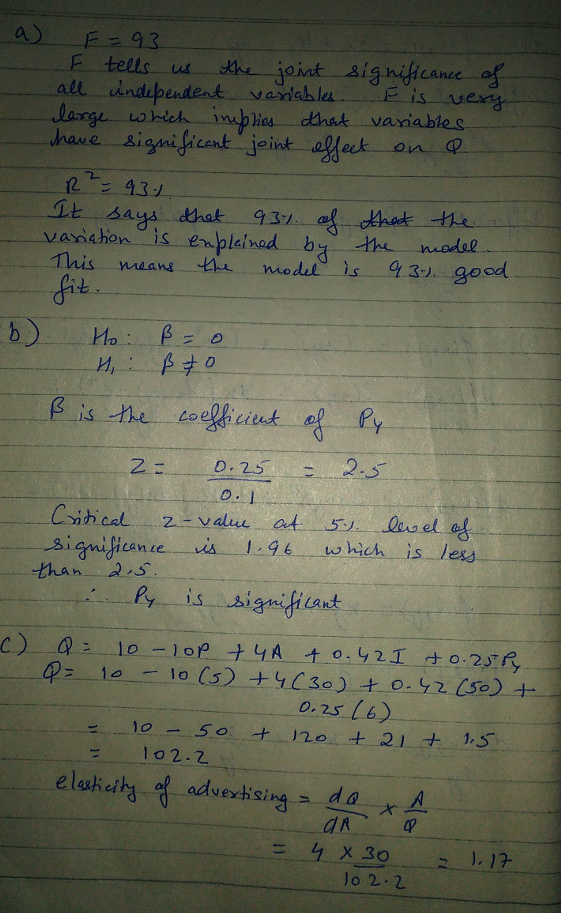
You might also like to view...
In considering the costs involved for student loans that must be repaid in ten years, this Application is addressing the economic concept of
A) the principle of diminishing returns. B) the real-nominal principle. C) the marginal principle. D) the principle of voluntary exchange.
Suppose the government has a budget deficit of $2 billion. If there is no Ricardo-Barro effect, how much crowding out of investment occurs?
A) some crowding out occurs, but less than $2 billion B) more than $2 billion C) exactly equal to $2 billion dollars D) No crowding out occurs and investment does not change. E) No crowding out occurs because investment increases.
Which of the following can be considered as a cultural barrier to trade?
a. Prohibition on Zimbabwean aircrafts from flying over or landing in Canada b. Restriction on the export of luxury goods to the Democratic Peoples Republic of Korea from Canada c. An arms embargo imposed on China by the U.K. government d. Japanese law requiring a new retail firm to receive permission from other retailers in the area in order to open a business e. Restriction on the export of strategic goods to Ghana imposed by the government of U.K
The contagion that spread to South Korea, Indonesia, and other countries during the Asian financial crisis was:
A. speculative attacks forcing them to abandon their fixed exchange rates. B. competitive devaluation that led to plummeting exchange rates for all. C. competitive revaluation that led to severe overvaluation and collapse for all but South Korea. D. a result of employing a fixed exchange rate by China.