Refer to the graph shown. The shift in the graph from D1 to D2 shows how a contractionary U.S. fiscal policy can cause a decrease in: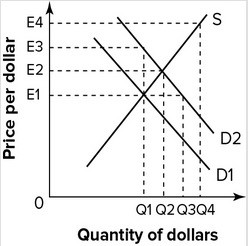
A. prices that raises the dollar's value.
B. interest rates that raises the dollar's value.
C. interest rates that reduces the dollar's value.
D. prices that reduces the dollar's value.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Does a rise in the price level bring a movement along the aggregate supply curve or does it shift the aggregate supply curve?
What will be an ideal response?
Your roommate argues that he can think of no better situation than living in a deflationary economy, as prices of goods and services would continuously fall. You disagree and argue that during a deflation, people can be made worse off because
A) the purchasing power of the currency would decrease. B) the value of the real interest rate will drop below the nominal interest rate. C) borrowers will have to pay increasing amounts in real terms over time. D) the purchasing power of people's incomes would increase.
Economists who identify a goal and then design a mechanism to achieve that goal are engaging in:
A. choice architecture. B. laissez-faire policies. C. setting money prices. D. mechanism design.
If the tax multiplier is -8.42, then the government purchases multiplier
A. is 9.42. B. is 8.42. C. is 1.58. D. cannot be determined because the MPS is not given.