Factor out the largest common factor.3x - 15
A. 3(3x - 5)
B. 3(x - 5)
C. 3(x - 15)
D. 15(x - 1)
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Determine an appropriate viewing window for the given function and use it to display its graph.f(x) = 
A. 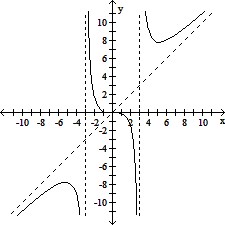
B. 
C. 
D. 
Use the graph of the function f(x) to locate the local extrema and identify the intervals where the function is concave up and concave down.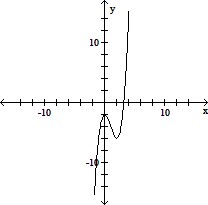
A. Local minimum at x = 0; local maximum at x = 2; concave down on (0, ?); concave up on (-?, 0) B. Local minimum at x = 0; local maximum at x = 2; concave up on (0, ?); concave down on (-?, 0) C. Local minimum at x = 2; local maximum at x = 0; concave down on (0, ?); concave up on (-?, 0) D. Local minimum at x = 2; local maximum at x = 0; concave up on (0, ?); concave down on (-?, 0)
The graph of either a cubic or quartic polynomial f(x) with leading coefficient ±1 and integer zeros is shown. Write the complete factored form of f(x).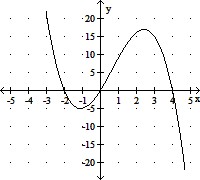
A. f(x) = x(x - 2)(x + 4) B. f(x) = -x(x - 2)(x + 4) C. f(x) = -x(x + 2)(x - 4) D. f(x) = x(x + 2)(x - 4)
The function f is one-to-one. State the domain and the range of f and f-1. Write the domain and range in set-builder notation.f(x) = -4x + 5
A. f(x): D = {x|x > -4}, R = {y|y > 5}; f-1(x): D = {x|x < -4}, R = {y|y < 5} B. f(x): D is all real numbers, R = {y|y > 5}; f-1(x): D is all real numbers, R = {y|y < 5} C. f(x): D is all real numbers, R is all real numbers; f-1(x): D is all real numbers, R is all real numbers D. f(x): D = {x|x > -4}, R is all real numbers; f-1(x): D = {x|x < -4}, R is all real numbers