A compound has the follOwing physical properties:
Critical Temperature = 1000 K
Critical Pressure = 20 atm
Boiling temperature at atmospheric pressure = 300 K
Molar Volume of saturated liquid at atmospheric pressure = 0.1 L/mol
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion for LIQUID is constant at 0.001 K-1
Isothermal Compressibility of LIQUID is constant at 5x10-4atm-1
Ideal Gas Heat Capacity is Cp*= 4R
Heat capacity in the liquid phase is constant at Cv=0.3 L atm/mol K,
In the gas/vapor phase, can be described by the equation of state:
PV = RT + (BP3)
Where B = 0.05 L mol-1atm-2
A) A stream of vapor enters a turbine at T=800 K and P=10 atm, and it leaves at T=500 K and P=2 atm. Find ?H and ?S for the vapor in this process.
B) Derive general equations (i.e., valid for any fluid, not just this compound) that express ((??H)/(??V))_Tand ((??H)/?T)_?Ventirely in terms of measureable properties. Your expressions can include P, V, T, CP, CV, and/or their derivatives, as well as the gas constant R.
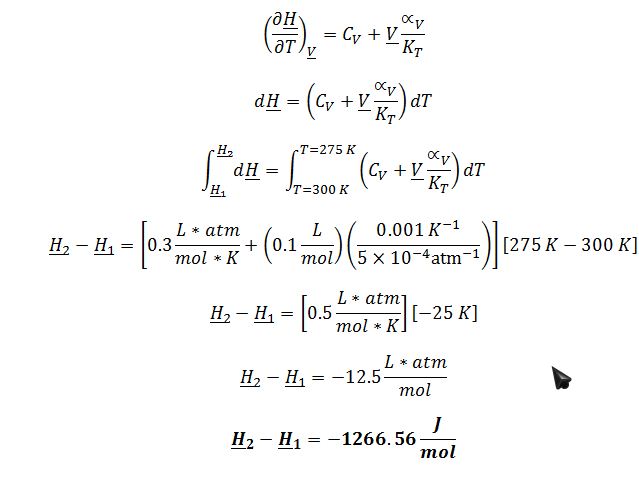
C) The compound described above, initially in the liquid phase at T=300 K and P=1 atm, is placed in a rigid container and cooled to T=275 K. What is the change in molar enthalpy of the compound for this process?
Apply definition of change in enthalpy of a gas including residual properties:
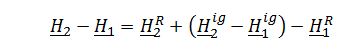
Evaluate ?H_1^Rand ?H_2^R, integrating residual enthalpy expression with respect to P:
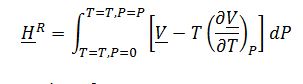
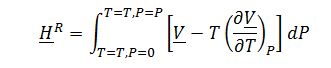
Where ?V is derived from the equation of state:
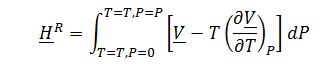
Evaluate ((??V)/?T)_P:
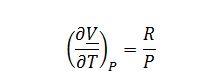
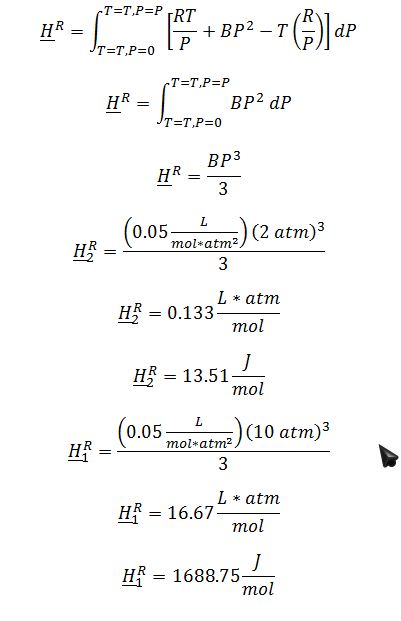
Substitute ((??V)/?T)_P and ?V into ?H^R expression all in terms of R, P, B, and T:
Evaluate ?H_2^ig-?H_1^ig:
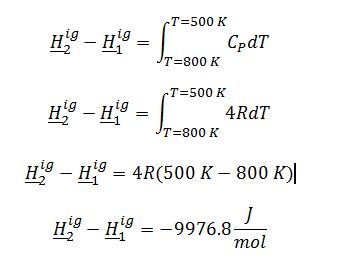
Substitute into change in enthalpy of a gas equation:
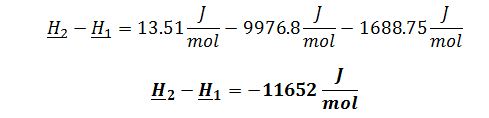
Apply definition of change in entropy of a gas including residual properties:
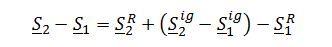
Evaluate residual entropy of gas, integrating with respect to dP:
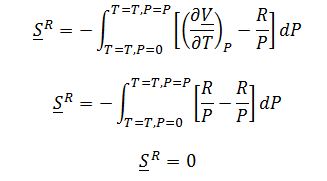
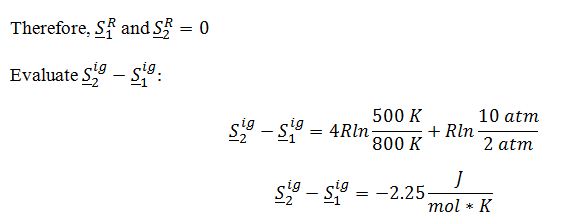
Substitute into total change in entropy of a gas equation:
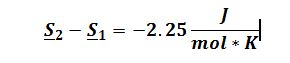
To derive expression for ((??H)/(??V))_Tin terms of measurable properties, start by applying the expansion rule:
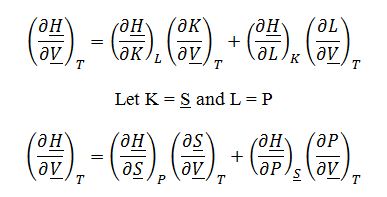
Where ((??H)/(??S))_P=T and ((??H)/?P)_?S=?V from the fundamental property relationship for change in enthalpy:
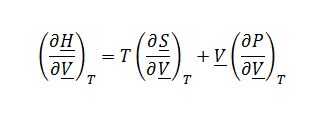
Where ((??S)/(??V))_T=(?P/?T)_?Vfrom Maxwell’s relationships:
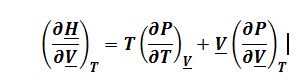
One could also obtain a valid answer in terms of isothermal compressibility and coefficient of
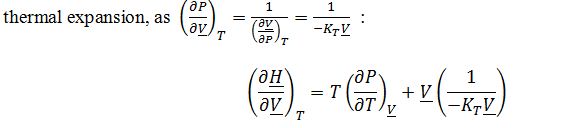
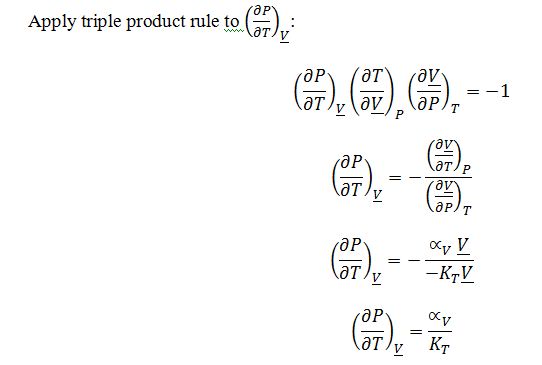
Substitute into ((??H)/(??V))_Texpression:
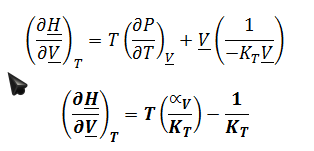
To derive expression for ((??H)/?T)_?Vin terms of measurable properties, start by applying the expansion rule:
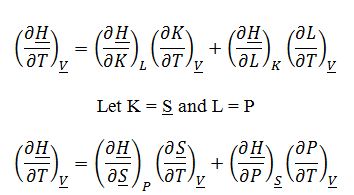
Where ((??H)/(??S))_P=T and ((??H)/?P)_?S=?V from the fundamental property relationship for change in enthalpy:
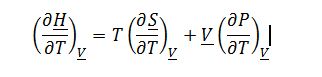
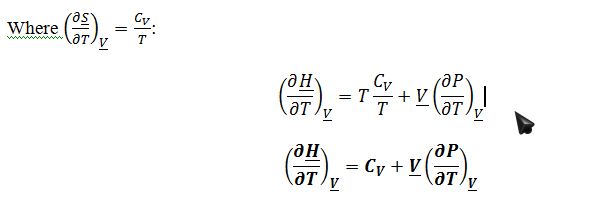
Again one can also express a valid answer in terms of isothermal compressibility and coefficient of thermal expansion, and this will be useful in part C. (?P/?T)_?V=?_V/K_T as derived previously:
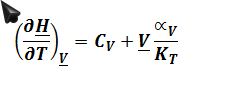
The process involves the changing of enthalpy at constant molar volume (rigid container) with changing temperature. Therefore, ((??H)/?T)_?V must be evaluated:
You might also like to view...
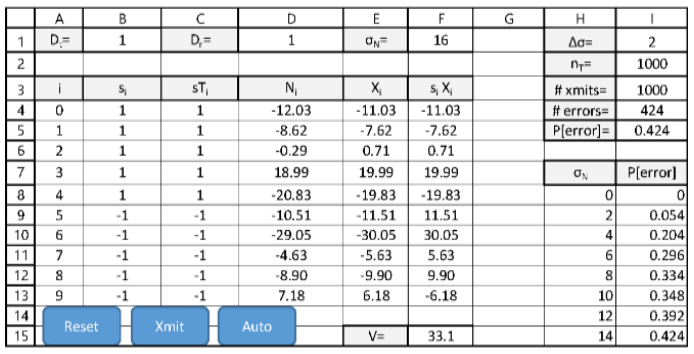
Probability of Error for complementary signals as function of ?N. The following worksheet specifies a 10-sample binary data signal s1 in B4:B13. A random transmitted bit Dt is computed in B1. The transmitted signal sTi (in C4:C13) = si if Dt=1 and =-si if Dt=0. The Gaussian noise sequence Ni SD ?N is specified in F1. The detected signal Xi is computed in E4:E13. The matched processor component siXi is computed in F4:F13, and the matched processor output V is computed in F15. The detected bit Dr is computed in D1.
The probability of error is estimated by computing the ratio of errors to transmitted data in I5 as
the noise ?N varies from 0 to 14?? in steps of ?? specified in I1. The total number of data bits to
be transmitted nT is specified in I2. The number of transmissions accomplished in shown in I3
and the number of errors in I4. Three VBA Macros are present:
? ResetCS resets the counts in I3 and I4.
? XmitCS increments the number of transmissions and, if an error occurs, increments the
error count.
? AutoCS computes the P[error] for nT transmissions as ?N varies and displays the results in
H8:I15.
a. What is the formula that computes Dt
in B1?
b. What is the formula that computes the transmitted signal sT2 in C6?
c. What is the formula that computes the noise component N2 in D6?
d. What is the formula that computes the detected signal X2 in E6?
e. What is the formula that computes the processor component s2X2 in F6?
f. What is the formula that computes the processor output V in F15?
g. What is the formula that computes Dr
in D1?
h. What is the formula that computes P[error] in I6 that produces 0 for #mits = 0?
i. Compose ResetCS.
j. Compose XmitCS.
k. Compose AutoCS.
If a = 7, b = 5, and c = 4, find the value of b(a + c)/(2a - c).
A. 4/5 B. 5 1/10 C. 5 5/11 D. 5 1/2
Even though smaller companies may not have a formal quality control program in place, a supervisor is still mainly responsible for _____.
a. researching standards b. building a quality job c. proving controls exist d. posting safety signs
Which of the following is the odd one out?
A. tappets B. lifters C. push tubes D. followers