The benefit that consumers get when they buy goods at the equilibrium price but were willing to pay more is called
A. Maximum price.
B. Consumer surplus.
C. Marginal utility.
D. The law of demand.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Which of the following would be an example of a public good?
a. A candy bar. b. A painting by Monet. c. A taxi cab. d. A sunset. e. The beach.
Country A has a higher money supply growth rate and a long-run Phillips curve that is farther to the left than country B's. In the long run as compared to country B, country A will have
a. lower unemployment and higher inflation b. higher unemployment and higher inflation c. lower unemployment and lower inflation d. None of the above is necessarily correct.
Suppose Firm A and Firm B are considering whether to invest in a new production technology. For each firm, the payoff to investing (given in thousands of dollars per day) depends upon whether the other firm invests, as shown in the payoff matrix below. 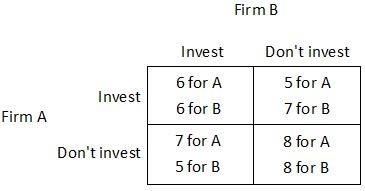 What is the Nash equilibrium of this game?
What is the Nash equilibrium of this game?
A. Firm A invests, and Firm B doesn't invest. B. Firm A invests, and Firm B invests. C. Firm A doesn't invest, and Firm B doesn't invest. D. Firm A doesn't invest, and Firm B invests.
Consider a small open economy in equilibrium with a zero current account balance. What happens to national saving, investment, and the current account balance in equilibrium if(a)future income rises?(b)business taxes rise?(c)government expenditures decline temporarily?(d)the future marginal product of capital rises?
What will be an ideal response?