The Earth is spherical, which causes differences in the intensity of solar radiation at different latitudes. The Earth is also titled on its axis at a 23.5? angle. How do you think this tilt affects the intensity of solar radiation?
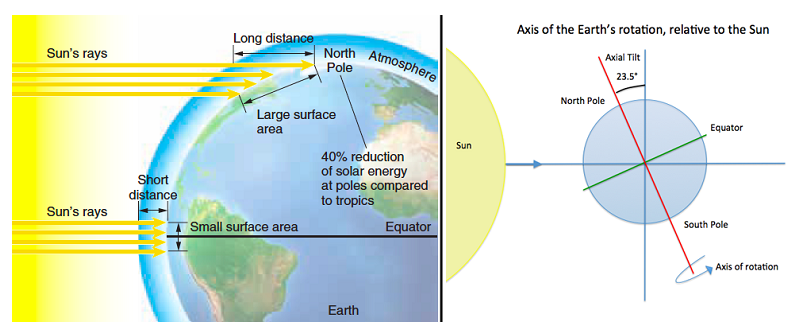
A. In the Northern and Southern hemispheres, equal latitudes receive the sun's rays at equal angles year round.
B. The Northern hemisphere has a lower intensity of solar radiation than the Southern hemisphere because it is tilted away from the Sun year round.
C. The sun's rays strike the Northern hemisphere more obliquely during its summer months and less obliquely during its winter months.
D. The Northern hemisphere has a higher intensity of solar radiation than the Southern hemisphere because it is tilted toward the Sun year round.
E. The sun's rays strike the Northern hemisphere more obliquely during its winter months and less obliquely during its summer months.
E. The sun's rays strike the Northern hemisphere more obliquely during its winter months and less obliquely during its summer months.
You might also like to view...
You have performed the following mating experiment using Hfr and F- strains of Escherichia coli: Hfr (thr+ leu+ gal+ strs) à— F- (thr- leu- gal- strr). Which of the following selective media would you use to score recombinant colonies?
A) minimal medium B) minimal medium + streptomycin C) minimal medium + threonine D) minimal medium + streptomycin + threonine
A stamen is
a. composed of a stigma, a style, and an ovary. b. the mature male gametophyte. c. the site where microspores are produced. d. part of the vegetative phase of an angiosperm. e. none of these.
Use of succinylcholine as an anaesthetic is very dangerous for people with a genotype for the fastacting
form of the enzyme serum cholinesterase Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
A portion (location) of DNA that encodes a specific protein is a Select one:
a. chromatid. b. kinetochore. c. centromere. d. gene. e. chromosome.