If a consumer is choosing the optimal combinations of two goods X and Y, and then the price of good Y decreases, this causes:
A. MU/P of good X to increase, so the consumer now must buy more X to find a new optimal combination.
B. demand for good X to increase.
C. MU/P of good Y to increase, so the consumer now must buy more Y to find a new optimal combination.
D. MU/P of good Y to decrease, so the consumer now must buy more Y to find a new optimal combination.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, an increase in government spending that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ creating _____gap. 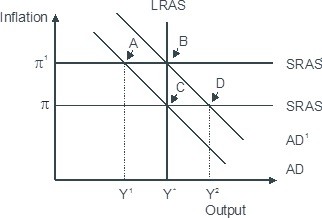
A. D; an expansionary B. B; no output C. B; expansionary D. A; a recessionary
Refer to Figure 10-5. Suppose the price of pizza increases while the price of hamburger remains constant. Then, the consumer's
A) indifference curve becomes straighter. B) budget constraint moves outward away from the origin on the pizza axis while the hamburger intercept remains the same. C) indifference curve becomes more concave away from the origin. D) budget constraint moves inward toward the origin on the pizza axis while the hamburger intercept remains the same.
Changes in business inventories are:
A. classified as investment expenditures. B. classified as government purchases. C. classified as consumption expenditures. D. excluded from GDP.
The CPI is a useful index for all of the following reasons except
A. it is used to determine whether people's incomes are keeping up with the costs of the things they buy. B. it is used to measure changes in the cost of living. C. it used to measure the average price level of all final goods and services produced. D. it is used to compute the U.S. inflation rate.