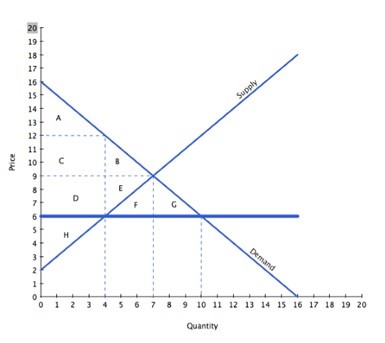
 With reference to the graph above, if the intended aim of the price ceiling set at $6 was a net increase in the well-being of consumers, then normative analysis would conclude that:
With reference to the graph above, if the intended aim of the price ceiling set at $6 was a net increase in the well-being of consumers, then normative analysis would conclude that:
A. the policy was effective, since surplus lost by producers through lower prices is less than the surplus gained by consumers through lower prices.
B. there is no "right" conclusion to be reached (in a normative sense), since people have different opinions concerning what constitutes a better outcome.
C. the policy was ineffective, since surplus gained by consumers through lower prices is less than the surplus they lost through deadweight loss.
D. the policy was effective, since surplus gained by consumers through lower prices is less than the surplus they lost through deadweight loss.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
When aggregate planned expenditure exceeds real GDP,
A) an unplanned increase in inventories occurs. B) real GDP remains at its equilibrium level. C) firms decrease production. D) an unplanned decrease in inventories occurs. E) real GDP decreases.
What are Pigouvian taxes and subsidies? How do governments decide when to levy a tax or provide a subsidy?
What will be an ideal response?
Max Shreck, an accountant, quit his $80,000-a-year job and bought an existing tattoo parlor from its previous owner, Sylvia Sidney. The lease has five years remaining and requires a monthly payment of $4,000. The lease
A) is a variable cost of operating the tattoo parlor. B) is an implicit cost of operating the tattoo parlor. C) is a fixed cost of operating the tattoo parlor. D) is part of the marginal cost of operating the tattoo parlor.
In 1900, the country with the highest per capita GDP was
A) Australia. B) New Zealand. C) the United States. D) Belgium. E) the Netherlands.