Suppose the price of one euro is fixed at $1.00. A Dutch oil company discovers new oil reserves in the North Sea and offers the oil for sale. What event would prevent a shortage of euros from developing?
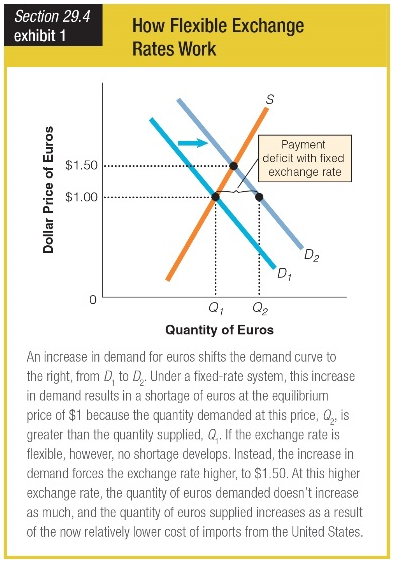
a. The dollar price of one euro remains fixed at $1.00.
b. The quantity of euros demanded changes from Q1 to Q2.
c. The dollar price of one euro is allowed to change to $1.50.
d. An increase in demand for euros shifts D1 to D2.
c. The dollar price of one euro is allowed to change to $1.50.
You might also like to view...
Arguing that economic growth will eventually stop because we will run out of natural resources:
A. ignores the power of markets to recognize shortages and induce changes in behavior. B. must be correct because scarcity exists. C. is supported today by the fact that richer countries have fewer natural resources. D. will only be correct if growth takes the form of newer, more efficient goods and services.
An 18 percent increase in the price of small cars results in a 10 percent expansion in the quantity supplied. The supply elasticity in this range equals ________
A) 9/5 B) 5/9 C) 7/10 D) 4/10
If economic profits are negative
A) accounting profits can be positive. B) accounting profits can be negative. C) the cost of capital is not being covered. D) all of these choices.
In a free-market economy, the pricing mechanism always operates to
a. produce an equitable distribution of income. b. provide an efficient allocation of resources. c. correct any inequality in distribution of output. d. equate consumers' desires with ability to pay.