Refer to the information provided in Figure 3.7 below to answer the following question(s).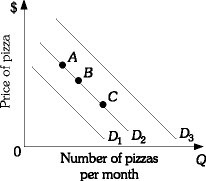 ?Figure 3.7Refer to Figure 3.7. Assume the market is initially at Point B and that pizza is a normal good. A decrease in income would cause the market to move from Point B on demand curve D2 to
?Figure 3.7Refer to Figure 3.7. Assume the market is initially at Point B and that pizza is a normal good. A decrease in income would cause the market to move from Point B on demand curve D2 to
A. demand curve D1.
B. demand curve D3.
C. Point A on demand curve D2.
D. Point C on demand curve D2.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Whenever external costs exist:
A.) Social demand is less than market demand. B.) Market demand is less than social demand. C.) Market demand and social demand are equal. D.) Market demand understates the social benefits.
According to the textbook, the best possible solution to the problem of poverty is:
A. the complete elimination of all efforts to assist the poor. B. a negative income tax with the tax credit equal to the poverty threshold. C. to maintain the current system. D. a combination of a negative income tax and public employment.
Suppose the demand for Pepsi-Cola is qp = 54 - 2pp + 1pc. The demand for Coca-Cola is qc = 54 - 2pc + 1pp. Each firm faces a constant marginal cost of zero. Determine the Bertrand equilibrium prices. What happens to the Bertrand equilibrium prices and profits if increased differentiation causes the demand for Pepsi-Cola to become qp = 104 - 2pp + 1pc while the demand for Coca-Cola remains
unchanged? What will be an ideal response?
In a flexible exchange-rate system, the value of a currency is determined by
A. Swiss gnomes. B. the demand and supply for the currency in the foreign exchange market. C. the government. D. the intersection of the IS and LM curves.