Explain why it is a common misconception that Galileo faced the Inquisition for his belief in a heliocentric Universe
What will be an ideal response?
It is assumed that Galileo faced the Inquisition because his book, Dialogo, which confronts the Aristotle/Ptolemaic model of a geocentric universe with the Copernican model of a heliocentric universe. The pope ordered Galileo to face Inquisition after he read a passage in Galileo's book disrespecting his own argument of God's omnipotence.
The Inquisition did not center on his belief in Copernican model, but rather, the trial centered on the instructions given Galileo in 1616 . From his file in the Vatican, his accusers produced a record of the meeting between Galileo and Cardinal Bellarmine that included the statement that Galileo was "not to hold, teach, or defend in any way" the principles of Copernicus. Therefore, The Inquisition condemned Galileo not for heresy but for disobeying the orders given him in 1616.
You might also like to view...
Snell's Law: A ray of light (ray a) in air strikes a flat piece of glass at an angle of ?0 = 84° with respect to the normal, as shown in the figure. The index of refraction of the glass is 1.5. What is the angle ? between the reflected ray (ray b) and refracted ray (ray c) rays? 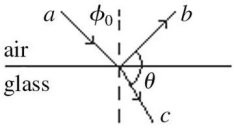
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
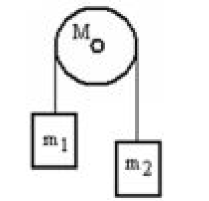
A mass src="https://sciemce.com/media/4/67174e56c9eba0e835.png" class="w-image" />?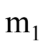 is connected by a light string that passes over a pulley of mass M to a mass
is connected by a light string that passes over a pulley of mass M to a mass 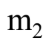 as shown in the figure. Both masses move vertically and there is no slippage between the string and the pulley. The pulley has a radius of 20.0 cm and a moment of inertia of 1?2
as shown in the figure. Both masses move vertically and there is no slippage between the string and the pulley. The pulley has a radius of 20.0 cm and a moment of inertia of 1?2 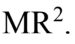 If
If 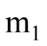 is 3.00 kg,
is 3.00 kg,  is 6.00 kg and M is 4.00 kg, then what is the tension in the string that is attached to mass
is 6.00 kg and M is 4.00 kg, then what is the tension in the string that is attached to mass
A. 33.6 N
B. 42.8 N
C. 53.6 N
D. 63.4 N
E. 75.5 N
A 100-m long transmission cable is suspended between two towers. If the mass density is 2.01 kg/m and the tension in the cable is 3.00 × 104 N, what is the speed of transverse waves on the cable?
A. 60 m/s B. 122 m/s C. 244 m/s D. 310 m/s E. 1500 m/s
What type of faulting results from expansive stresses?
a. Reverse b. Normal c. Strike-slip d. Abnormal