Explain why a change in income tax rates causes the consumption schedule to change slope.
What will be an ideal response?
An income tax rate determines the portion of an increase in income that is taken in taxes. If the rate increases, then for any increase in income, disposable income increases by a smaller amount. When a portion of the increase in disposable income is consumed, the consumption spending is less than it would be if the income tax rate was lower. The smaller increase in consumption for a given increase in income means that the numerical value of the MPC is smaller, and the slope of the consumption schedule is flatter. Conversely, if the income tax rate decreases, then for any increase in income, disposable income increases by a larger amount. The larger increase in consumption for a change in income means that the numerical value of the MPC is larger and the consumption schedule is steeper.
You might also like to view...
The government passes a law which doubles the wages of all workers. Aggregate supply will ________, and real GDP will ________, and the price level will ________
A) increase; remain the same; increase. B) remain the same; increase; increase. C) increase; increase; remain the same. D) decrease; increase; increase. E) decrease; decrease; increase.
In year 1 the CPI is 175, and in year 2 the CPI is 189. If Dennis's salary was $82,000 in year 1, what is the minimum salary he must earn in year 2 to "keep up with inflation"?
a. $83,550 b. $92,360 c. $85,750 d. $88,560
If the short-term own price elasticity for food is estimated to be ?0.4, then long-term own price elasticity is expected to be:
A. greater than -0.4 (less elastic). B. ?0.4. C. less than -0.4 (more elastic). D. neither greater than, less than, nor equal to ?0.4.
In Figure 5.7, assuming perfect competition, at MR3 there will be 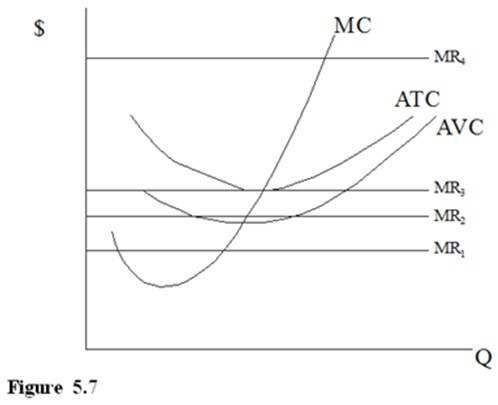
A. no pressure on the price to change. B. short-run pressure on the price to rise. C. short and long-run pressure on the price to rise. D. long-run pressure on the price to rise.